Judges 3:13
Bible Commentary
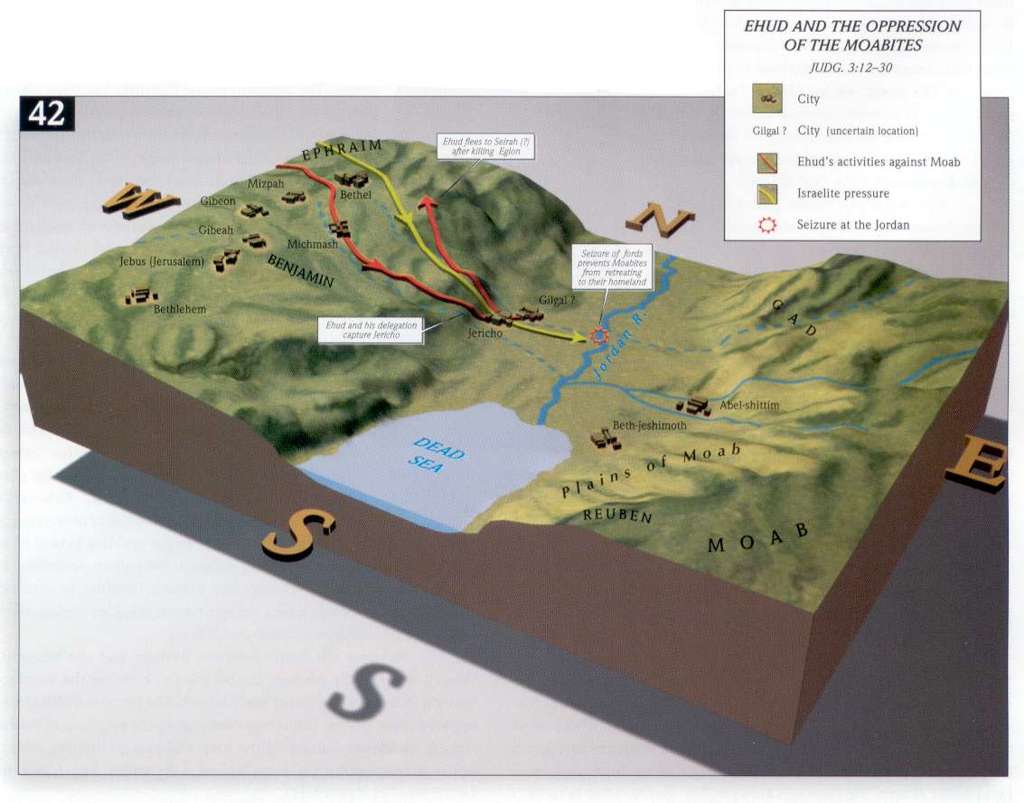
The city of palm trees - This the Targum renders the city of Jericho; but Jericho had been destroyed by Joshua, and certainly was not rebuilt till the reign of Ahab, long after this, 1 Kings 16:34. However, as Jericho is expressly called the city of palm trees, Deuteronomy 34:3, the city in question must have been in the vicinity or plain of Jericho, and the king of Moab had seized it as a frontier town contiguous to his own estates. Calmet supposes that the city of palm trees means En-gaddi.
Notes on the Whole Bible
The children of Ammon (Bent-Ammon), almost always so spoken of from their ancestor Ben-ammi Genesis 19:38, seem to be under the leadership of the king of Moab, as do also the Amlekites: this is perhaps the strengthening spoken of in Judges 3:12. In Judges 11:24. The Amalekites appear as the constant and bitter foes of the Israelites (Exodus 17:8 notes and references); and the naming a mountain in Ephraim, “the mount of the Amalekites” Judges 12:15 is probably a memorial of this joint invasion of Moabites and Amalekites, and marks the scene either of their occupation, or of some signal victory over them.
The city of palm trees: i. e. Jericho Judges 1:16, having been utterly destroyed by Joshua, and not rebuilt until the time of Ahab Joshua 6:24-26; 1 Kings 16:34, can only have existed at this time as an unwalled village, - like Jerusalem after its destruction by Nebuzaradan, until Nehemiah rebuilt its waits - and like its modern representative er-Riha, a village with a fortress for the Turkish garrison. This occupation of Jericho should be compared with the invasion in Judges 10:9, where two out of the three tribes named, Benjamin and Ephraim, are the same as those here concerned, and where Judges 10:7 the Philistines are coupled with the Ammonites, just as here Judges 3:31 the Philistines are mentioned in near connection with the Moabites. See Introduction.
Concise Bible Commentary
Patriarchs and Prophets, 545
“They forsook the Lord God of their fathers, which brought them out of the land of Egypt,” “and guided them in the wilderness like a flock.” “They provoked Him to anger with their high places, and moved Him to jealousy with their graven images.” Therefore the Lord “forsook the tabernacle of Shiloh, the tent which He placed among them; and delivered His strength into captivity, and His glory into the enemy's hand.” Judges 2:12; Psalm 78:52, 58, 60, 61. Yet He did not utterly forsake His people. There was ever a remnant who were true to Jehovah; and from time to time the Lord raised up faithful and valiant men to put down idolatry and to deliver the Israelites from their enemies. But when the deliverer was dead, and the people were released from his authority, they would gradually return to their idols. And thus the story of backsliding and chastisement, of confession and deliverance, was repeated again and again. PP 545.1
The king of Mesopotamia, the king of Moab, and after them the Philistines, and the Canaanites of Hazor, led by Sisera, in turn became the oppressors of Israel. Othniel, Shamgar, and Ehud, Deborah and Barak, were raised up as deliverers of their people. But again “the children of Israel did evil in the sight of the Lord; and the Lord delivered them into the hand of Midian.” Heretofore the hand of the oppressor had fallen but lightly on the tribes dwelling east of the Jordan, but in the present calamities they were the first sufferers. PP 545.2
The Amalekites on the south of Canaan, as well as the Midianites on its eastern border, and in the deserts beyond, were still the unrelenting enemies of Israel. The latter nation had been nearly destroyed by the Israelites in the days of Moses, but they had since increased greatly, and had become numerous and powerful. They had thirsted for revenge; and now that the protecting hand of God was withdrawn from Israel, the opportunity had come. Not alone the tribes east of Jordan, but the whole land suffered from their ravages. The wild, fierce inhabitants of the desert, “as locusts for multitude” (Judges 6:5, R.V.), came swarming into the land, with their flocks and herds. Like a devouring plague they spread over the country, from the river Jordan to the Philistine plain. They came as soon as the harvests began to ripen, and remained until the last fruits of the earth had been gathered. They stripped the fields of their increase and robbed and maltreated the inhabitants and then returned to the deserts. Thus the Israelites dwelling in the open country were forced to abandon their homes, and to congregate in walled towns, to seek refuge in fortresses, or even to find shelter in caves and rocky fastnesses among the mountains. For seven years this oppression continued, and then, as the people in their distress gave heed to the Lord's reproof, and confessed their sins, God again raised up a helper for them. PP 545.3
Read in context »