Genesis 32:12
Bible Commentary
Make thy seed as the sand - Having come to the promise by which the covenant was ratified both to Abraham and Isaac, he ceased, his faith having gained strong confirmation in a promise which he knew could not fail, and which he found was made over to him, as it had been to his father and grandfather.
Notes on the Whole Bible
- Jacob Wrestles in Prayer
3. מחנים machănāyı̂m Machanaim, “two camps.”
22. יבק yaboq Jabboq; related: בקק bāqaq “gush or gurgle out” or אבק 'ābaq in niphal, “wrestle.” Now Wady Zurka.
29. ישׂראל yı̂śrā'ēl Jisrael, “prince of God.”
31. פניאל penı̂y'ēl = פנוּאל penû'ēl Peniel, Penuel, “face of God.”
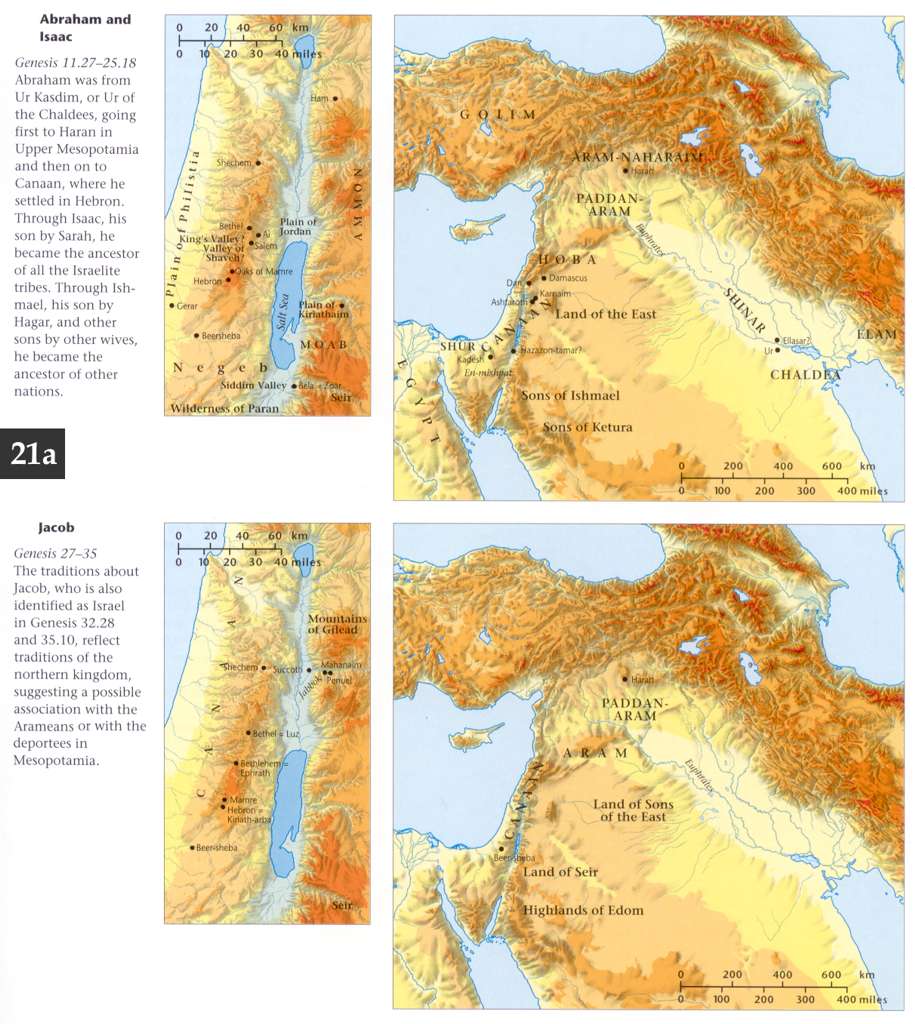
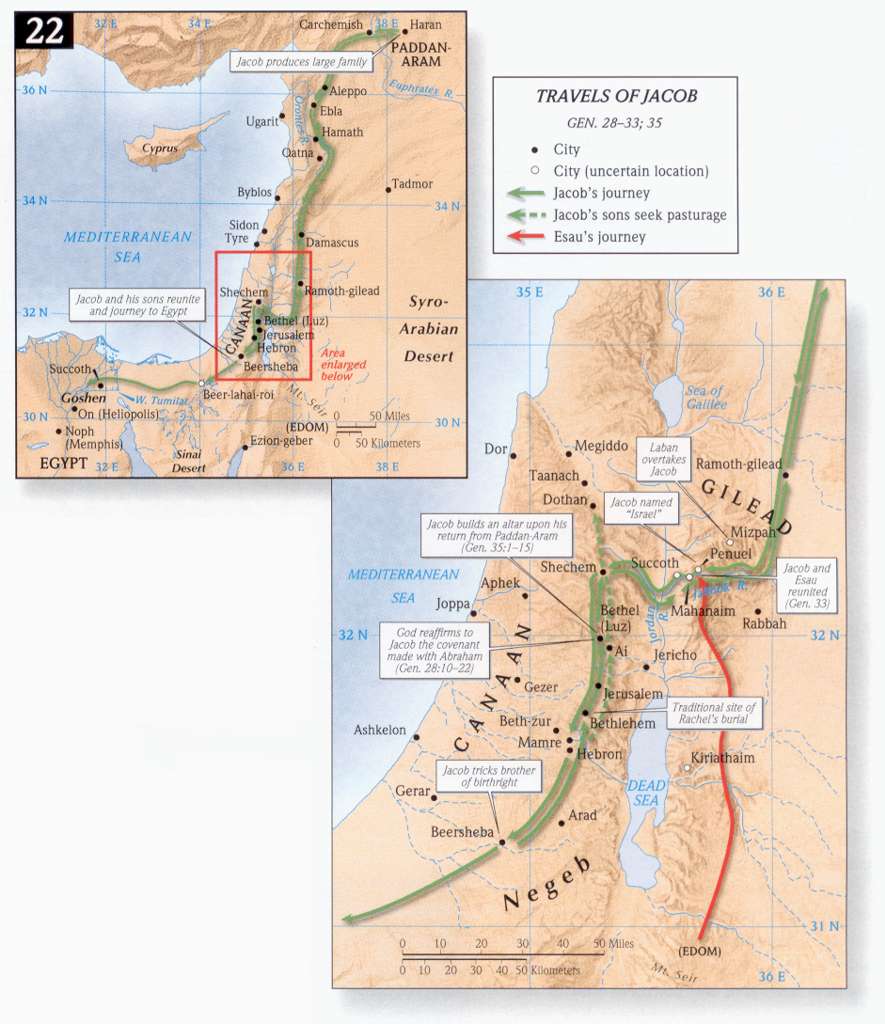
After twenty years spent in Aram, Jacob now returns to Kenann. As his departure was marked by a great moment in his spiritual life, so he is now approaching to a crisis in his life of no less significance
Genesis 32:1-3
Jacob has a vision of the heavenly host. This passage, recording Laban‘s farewell and departure, closes the connection of Jacob with Haran and all its toils of servitude, and is hence, annexed to the previous chapter in the English version. In the distribution of the original text, it is regarded as the counterpart of the two following verses, in which Jacob‘s onward progress is mentioned, and so placed with them at the beginning of a new chapter. “The angels of God met him.” Twenty years ago Jacob saw the mystical ladder connecting heaven and earth, and the angels of God thereupon ascending and descending from the one to the other. Now, in circumstances of danger, he sees the angels of God on earth, encamped beside or around his own camp Psalm 34:8. He recognizes them as God‘s camp, and names the place Mahanaim, from the double encampment. This vision is not dwelt upon, as it is the mere sequel of the former scene at Bethel. Mahanaim has been identified with Mahneh, about eight miles from the cairn of Laban and Jacob.
Genesis 32:4-9
Jacob now sends a message to Esau apprising him of his arrival. Unto the land of Seir. Arabia Petraea, with which Esau became connected by his marriage with a daughter of Ishmael. He was now married 56 years to his first two wives, and 20 to his last, and therefore, had a separate and extensive establishment of children and grandchildren. Jacob endeavors to make amends for the past by an humble and respectful approach to his older brother, in which he styles himself, “thy servant” and Esau, “my lord.” He informs him of his wealth, to intimate that he did not expect anything from him. “Four hundred men with him.” This was a formidable force. Esau had begun to live by the sword Genesis 27:40, and had surrounded himself with a numerous body of followers. Associated by marriage with the Hittites and the Ishmaelites, he had rapidly risen to the rank of a powerful chieftain. It is vain to conjecture with what intent Esau advanced at the head of so large a retinue. It is probable that he was accustomed to a strong escort, that he wished to make an imposing appearance before his brother, and that his mind was in that wavering state, when the slightest incident might soothe him into good-will, or arouse him to vengeance. Jacob, remembering his own former dealings with him, has good cause for alarm. He betakes himself to the means of deliverance. He disposes of his horde into two camps, that if one were attacked and captured, the other might meanwhile escape. He never neglects to take all the precautions in his power.
Genesis 32:10-13
Next, he betakes himself to prayer. He appeals to the God of Abraham and Isaac, to Yahweh the God of promise and performance. “I am less than;” unworthy of all the mercy and truth of God. “With my staff.” Jacob seems to have left his home without escort and without means. It was evidently intended that he should return in a short time; but unforeseen circumstances lengthened the period. “Me, the mother with the children.” Me is used here in that pregnant sense which is familiar in Scripture, to include his whole clan; as Ishmael, Israel, Edom, often stand for their respective races. He then pleads the express promise of God Genesis 28:13-15; Genesis 31:3.
Genesis 32:14-22
Jacob sends forward a present to Esau. “He lodged there that night.” Mahanaim may have been about twenty-five miles from the Jabbok. At some point in the interval he awaited the return of his messengers. Abiding during the night in the camp, not far from the ford of the Jabbok, he selects and sends forward to Esau his valuable present of five hundred and fifty head of cattle. “That which was come into his hand,” into his possession. The cattle are selected according to the proportions of male and female which were adopted from experience among the ancients (Varro, de re rust. II. 3). “Every drove by itself,” with a space between, that Esau might have time to estimate the great value of the gift. The repetition of the announcement of the gift, and of Jacob himself being at hand, was calculated to appease Esau, and persuade him that Jacob was approaching him in all brotherly confidence and affection. “Appease him.” Jacob designs this gift to be the means of propitiating his brother before he appears in his presence. “Lift up my face,” accept me. “Lodged that night in the camp;” after sending this present over the Jabbok. This seems the same night referred to in Genesis 32:14.
Genesis 32:23-32
Jacob wrestles with a man. “Passed over the ford of Jabbok.” The Jabbok rose near Rabbath Ammon, and flowed into the Jordan, separating North Gilead from South, or the kingdom of Og from that of Sihon. “Jacob was left alone,” on the north side, after all had passed over. “A man wrestled with him.” When God has a new thing of a spiritual nature to bring into the experience of man, he begins with the senses. He takes man on the ground on which he finds him, and leads him through the senses to the higher things of reason, conscience, and communion with God.
Jacob seems to have gone through the principles or foundations of faith in God and repentance toward him, which gave a character to the history of his grandfather and father, and to have entered upon the stage of spontaneous action. He had that inward feeling of spiritual power which prompted the apostle to say, “I can do all things.” Hence, we find him dealing with Esau for the birthright, plotting with his mother for the blessing, erecting a pillar and vowing a vow at Bethel, overcoming Laban with his own weapons, and even now taking the most prudent measures for securing a welcome from Esau on his return. He relied indeed on God, as was demonstrated in many of his words and deeds; but the prominent feature of his character was a strong and firm reliance on himself. But this practical self-reliance, though naturally springing up in the new man and highly commendable in itself, was not yet in Jacob duly subordinated to that absolute reliance which ought to be placed in the Author of our being and our salvation. Hence, he had been betrayed into intrusive, dubious, and even sinister courses, which in the retributive providence of God had brought, and were yet to bring him, into many troubles and perplexities. The hazard of his present situation arose chiefly from his former unjustifiable practices toward his brother. He is now to learn the lesson of unreserved reliance on God.
“A man” appeared to him in his loneliness; one having the bodily form and substance of a man. Wrestled with him - encountered him in the very point in which he was strong. He had been a taker by the heel from his very birth, and his subsequent life had been a constant and successful struggle with adversaries. And when he, the stranger, saw that he prevailed not over him. Jacob, true to his character, struggles while life remains, with this new combatant. touched the socket of his thigh, so that it was wrenched out of joint. The thigh is the pillar of a man‘s strength, and its joint with the hip the seat of physical force for the wrestler. Let the thigh bone be thrown out of joint, and the man is utterly disabled. Jacob now finds that this mysterious wrestler has wrested from him, by one touch, all his might, and he can no longer stand alone. Without any support whatever from himself, he hangs upon the conqueror, and in that condition learns by experience the practice of sole reliance on one mightier than himself. This is the turning-point in this strange drama. Henceforth Jacob now feels himself strong, not in himself, but in the Lord, and in the power of his might. What follows is merely the explication and the consequence of this bodily conflict.
And he, the Mighty Stranger, said, Let me go, for the dawn ariseth. The time for other avocations is come: let me go. He does not shake off the clinging grasp of the now disabled Jacob, but only calls upon him to relax his grasp. “And he, Jacob, said, I will not let thee go except thou bless me”. Despairing now of his own strength, he is Jacob still: he declares his determination to cling on until his conqueror bless him. He now knows he is in the hand of a higher power, who can disable and again enable, who can curse and also bless. He knows himself also to be now utterly helpless without the healing, quickening, protecting power of his victor, and, though he die in the effort, he will not let him go without receiving this blessing. Jacob‘s sense of his total debility and utter defeat is now the secret of his power with his friendly vanquisher. He can overthrow all the prowess of the self-reliant, but he cannot resist the earnest entreaty of the helpless.
Genesis 32:28-30
“What is thy name?” He reminds him of his former self, Jacob, the supplanter, the self-reliant, self-seeking. But now he is disabled, dependent on another, and seeking a blessing from another, and for all others as well as himself. No more Jacob shall thy name be called, but Israel - a prince of God, in God, with God. In a personal conflict, depending on thyself, thou wert no match for God. But in prayer, depending on another, thou hast prevailed with God and with men. The new name is indicative of the new nature which has now come to its perfection of development in Jacob. Unlike Abraham, who received his new name once for all, and was never afterward called by the former one, Jacob will hence, be called now by the one and now by the other, as the occasion may serve. For he was called from the womb Genesis 25:23, and both names have a spiritual significance for two different aspects of the child of God, according to the apostle‘s paradox, “Work out your own salvation with fear and trembling, for it is God that worketh in you both to will and to do of his good pleasure” Philemon 2:12-13. “Tell now thy name.”
Disclose to me thy nature. This mysterious Being intimates by his reply that Jacob was to learn his nature, so far as he yet required to know it, from the event that had just occurred; and he was well acquainted with his name. And he blessed him there. He had the power of disabling the self-sufficient creature, of upholding that creature when unable to stand, of answering prayer, of conferring a new name, with a new phase of spiritual life, and of blessing with a physical renovation, and with spiritual capacity for being a blessing to mankind. After all this, Jacob could not any longer doubt who he was. There are, then, three acts in this dramatic scene: first, Jacob wrestling with the Omnipresent in the form of a man, in which he is signally defeated; second, Jacob importunately supplicating Yahweh, in which he prevails as a prince of God; third, Jacob receiving the blessing of a new name, a new development of spiritual life, and a new capacity for bodily action.
Genesis 32:31-32
Peniel - the face of God. The reason of this name is assigned in the sentence, “I have seen God face to face.” He is at first called a man. Hosea terms him the angel (Hosea 12:4-5 (3,4). And here Jacob names him God. Hence, some men, deeply penetrated with the ineffable grandeur of the divine nature, are disposed to resolve the first act at least into an impression on the imagination. We do not pretend to define with undue nicety the mode of this wrestling. And we are far from saying that every sentence of Scripture is to be understood in a literal sense. But until some cogent reason be assigned, we do not feel at liberty to depart from the literal sense in this instance. The whole theory of a revelation from God to man is founded upon the principle that God can adapt himself to the apprehension of the being whom he has made in his own image. This principle we accept, and we dare not limit its application “further than the demonstrative laws of reason and conscience demand.” If God walk in the garden with Adam, expostulate with Cain, give a specification of the ark to Noah, partake of the hospitality of Abraham, take Lot by the hand to deliver him from Sodom, we cannot affirm that he may not, for a worthy end, enter into a bodily conflict with Jacob. These various manifestations of God to man differ only in degree. If we admit anyone, we are bound by parity of reason to accept all the others.
We have also already noted the divine method of dealing with man. He proceeds from the known to the unknown, from the simple to the complex, from the material to the spiritual, from the sensible to the super-sensible. So must he do, until he have to deal with a world of philosophers. And even then, and only then, will his method of teaching and dealing with people be clearly and fully understood. The more we advance in the philosophy of spiritual things, the more delight will we feel in discerning the marvelous analogy and intimate nearness of the outward to the inward, and the material to the spiritual world. We have only to bear in mind that in man there is a spirit as well as a body; and in this outward wrestling of man with man we have a token of the inward wrestling of spirit with spirit, and therefore, an experimental instance of that great conflict of the Infinite Being with the finite self, which grace has introduced into our fallen world, recorded here for the spiritual edification of the church on earth.
“My life is preserved.” The feeling of conscience is, that no sinner can see the infinitely holy God and live. “And he halted upon his thigh.” The wrenching of the tendons and muscles was mercifully healed, so as to leave a permanent monument, in Jacob‘s halting gait, that God had overcome his self-will.
Concise Bible Commentary
The Story of Redemption, 92-3
Laban then assured Jacob that he had an interest for his daughters and their children, that he could not harm them. He proposed to make a covenant between them. And Laban said, “Now therefore come thou, let us make a covenant, I and thou; and let it be for a witness between me and thee. And Jacob took a stone, and set it up for a pillar. And Jacob said unto his brethren, Gather stones; and they took stones, and made an heap: and they did eat there upon the heap.” SR 92.1
And Laban said, “The Lord watch between me and thee, when we are absent one from another. If thou shalt afflict my daughters, or if thou shalt take other wives besides my daughters; no man is with us; see, God is witness betwixt me and thee.” SR 92.2
Jacob made a solemn covenant before the Lord that he would not take other wives. “And Laban said to Jacob, Behold this heap, and behold this pillar, which I have cast betwixt me and thee; this heap be witness, and this pillar be witness, that I will not pass over this heap to thee, and that thou shalt not pass over this heap and this pillar unto me, for harm. The God of Abraham, and the God of Nahor, the God of their father, judge betwixt us. And Jacob swear by the fear of his father Isaac.” SR 92.3
As Jacob went on his way, the angels of God met him. And when he saw them, he said, “This is God's host.” He saw the angels of God in a dream, encamping around about him. Jacob sent a humble, conciliatory message to his brother Esau. “And the messengers returned to Jacob, saying, We came to thy brother Esau, and also he cometh to meet thee, and four hundred men with him. Then Jacob was greatly afraid and distressed: and he divided the people that was with him, and the flocks, and herds, and the camels, into two bands; and said, If Esau come to the one company, and smite it, then the other company which is left shall escape. SR 92.4
Read in context »The Story of Redemption, 97
Jacob and Esau represent two classes: Jacob, the righteous, and Esau, the wicked. Jacob's distress when he learned that Esau was marching against him with four hundred men, represents the trouble of the righteous as the decree goes forth to put them to death, just before the coming of the Lord. As the wicked gather about them, they will be filled with anguish, for, like Jacob, they can see no escape for their lives. The angel placed himself before Jacob, and he took hold of the angel and held him and wrestled with him all night. So also will the righteous, in their time of trouble and anguish, wrestle in prayer with God, as Jacob wrestled with the angel. Jacob in his distress prayed all night for deliverance from the hand of Esau. The righteous in their mental anguish will cry to God day and night for deliverance from the hand of the wicked who surround them. SR 97.1
Jacob confessed his unworthiness: “I am not worthy of the least of all the mercies, and of all the truth, which Thou hast shewed unto Thy servant.” The righteous in their distress will have a deep sense of their unworthiness and with many tears will acknowledge their utter unworthiness and, like Jacob, will plead the promises of God through Christ, made to just such dependent, helpless, repenting sinners. SR 97.2
Jacob took firm hold of the angel in his distress and would not let Him go. As he made supplication with tears, the angel reminded him of his past wrongs and endeavored to escape from Jacob, to test and prove him. So will the righteous, in the day of their anguish, be tested, proved, and tried, to manifest their strength of faith, their perseverance and unshaken confidence in the power of God to deliver them. SR 97.3
Read in context »