Genesis 17:20
Bible Commentary
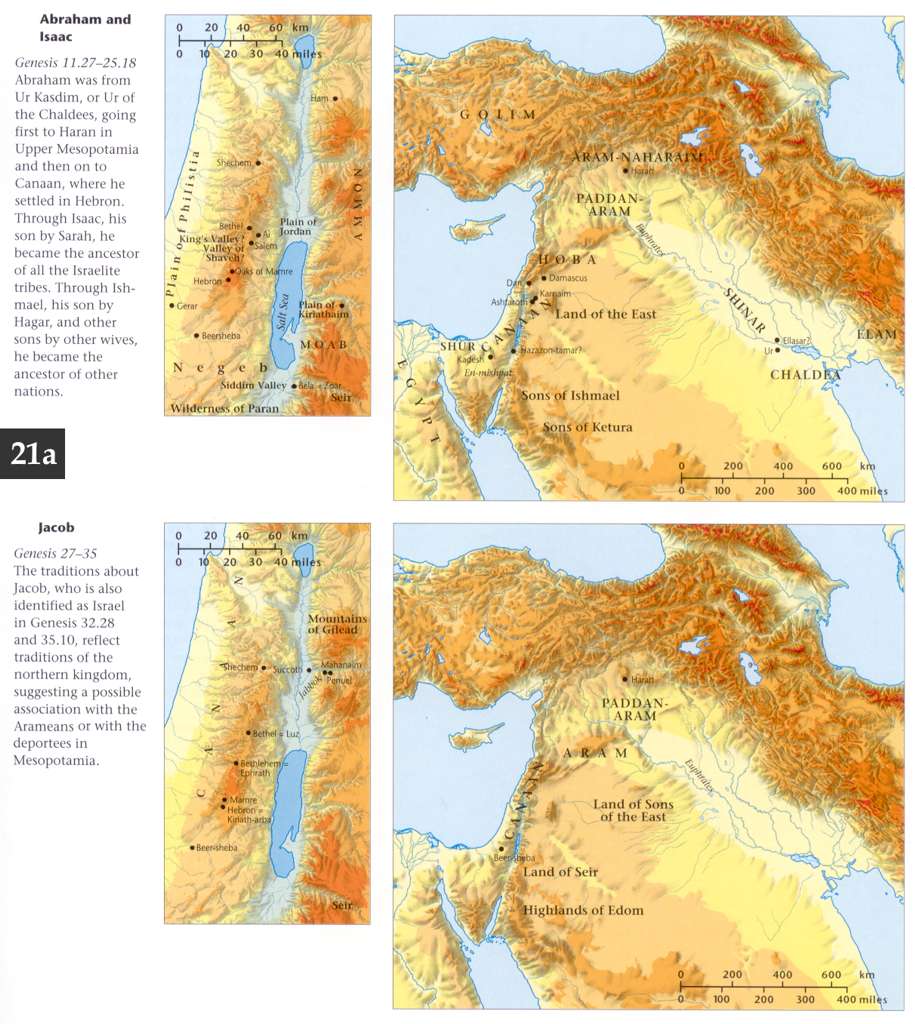
Twelve princes shall he beget, etc. - See the names of these twelve princes, Genesis 25:12-16. From Ishmael proceeded the various tribes of the Arabs, called also Saracens by Christian writers. They were anciently, and still continue to be, a very numerous and powerful people. "It was somewhat wonderful, and not to be foreseen by human sagacity," says Bishop Newton, "that a man's whole posterity should so nearly resemble him, and retain the same inclinations, the same habits, and the same customs, throughout all ages! These are the only people besides the Jews who have subsisted as a distinct people from the beginning, and in some respects they very much resemble each other 1. The Arabs, as well as the Jews, are descended from Abraham, and both boast of their descent from the father of the faithful. 2. The Arabs, as well as the Jews, are circumcised, and both profess to have derived this ceremony from Abraham. 3. The Arabs, as well as the Jews, had originally twelve patriarchs, who were their princes or governors. 4. The Arabs, as well as the Jews, marry among themselves, and in their own tribes. 5. The Arabs, as well as the Jews, are singular in several of their customs, and are standing monuments to all ages of the exactness of the Divine predictions, and of the veracity of Scripture history. We may with more confidence believe the particulars related of Abraham and Ishmael when we see them verified in their posterity at this day. This is having, as it were, ocular demonstration for our faith." See Bp. Newton's Second Dissertation on the Prophecies, and See note on Genesis 16:12.
Notes on the Whole Bible
- The Sealing of the Covenant
1. שׁדי shaday Shaddai, “Irresistible, able to destroy, and by inference to make, Almighty.” שׁדד shādad “be strong, destroy.” This name is found six times in Genesis, and thirty-one times in Job.
5. אברהם 'abrâhām Abraham, from אברם 'abrām “high-father,” and הם hām the radical part of המין hāmôn a “multitude,” is obtained by a euphonic abbreviation אברהם 'abrâhām “father of a multitude.” The root רהם rhm is a variation of רום rvm affording, however, a link of connection in sound and sense with the root המה hāmâh “hum, be tumultuous,” from which comes המון hāmôn a “multitude.” The confluence of the biliterals רם rm and הם hm yields the triliteral רהם rhm occurring in Arabic, though not elsewhere in our written Hebrew. The law of formation here noticed is interesting and real, though רהם rhm may not have been an actual result of it.
11. נמלתם nemaltem formed from נמל nāmal “circumcised.” מוּל mûl “cut, circumcise.”
15. שׂרה śārâh Sarah, “princess.”
19. יצהק yı̂tschāq Jitschaq, “laughing.”
The present form of the covenant is not identical with the former. That referred chiefly to the land; this chiefly to the seed. That dwelt much on temporal things; this rises to spiritual things. That specifies only Abram; this mentions both Abram and Sarai. At the former period God formally entered into covenant with Abram ברית כרת kārat berı̂yt Genesis 15:18); at present he takes the first step in the fufillment of the covenant ברית נתן nātan berı̂yt seals it with a token and a perpetual ordinance, and gives Abram and Sarai new names in token of a new nature. There was an interval of fourteen years at least between the ratification of the covenant and the preparation for the fulfillment of its conditions, during which Abraham‘s faith had time to unfold.
Genesis 17:1-8
The covenant in its spiritual aspect. “The Lord,” the Author of existence and performance. “God Almighty,” El Shaddai. “El,” the Lasting, Eternal, Absolute. “Shaddai,” the Irresistible, Unchangeable, Destructive Isaiah 13:6; Joel 1:15. This term indicates on the one hand his judicial, punitive power, and points to his holiness; and on the other hand, his alterative, reconstructive power, and points to his providence. The complex name, therefore, describes God as the Holy Spirit, who works in the development of things, especially in the punishment and eradication of sin and its works, and in the regeneration and defense of holiness. It refers to potence, and potence combined with promise affords ground for faith.
Walk before me and be perfect. - In the institution of the covenant we had “fear not” - an encouragement to the daunted or the doubting. In its confirmation we have a command, a rule of life, prescribed. This is in keeping with the circumstances of Abraham. For, first, he has now faith in the Lord, which is the fruit of the new man in him prevailing over the old, and is therefore competent to obey; and, next, the Lord in whom he believes is God Almighty, the all-efficient Spirit, who worketh both to will and to do in the destroying of sin and building up of holiness. “Walk” - act in the most comprehensive sense of the term; “before me,” and not behind, as one conscious of doing what is, not displeasing, but pleasing to me; “and be perfect,” not sincere merely, unless in the primitive sense of duty, but complete, upright, holy, not only in walk, which is provided for in the previous clause, but in heart, the spring of action.
Genesis 17:2
My covenant - which I have already purposed and formally closed. “I will grant,” carry into effect, the provisions of it. “Multiply thee.” The seed is here identified with the head or parent seat of life. The seed now comes forward as the prominent benefit of the covenant.
Genesis 17:3-6
Abram fell on his face. - This is the lowliest form of reverence, in which the worshipper leans on his knees and elbows, and his forehead approaches the ground. Prostration is still customary in the East. Abram has attained to loftier notions of God. “God talked with him.” Yahweh, El Shaddai, is here called God. The Supreme appears as the Author of existence, the Irresistible and Everlasting, in this stage of the covenant relation.
Genesis 17:4
As for me. - The one party to the covenant is here made prominent, as in Genesis 17:9 the other party is brought out with like emphasis. The exalted Being who has entered into it imparts a grandeur, solemnity, and excellence to the covenant. “Father of many nations.” The promise of seed is here expanded and particularized. A multitude of nations and kings are to trace their descent from Abram. This is true in a literal sense. The twelve tribes of Israel and many Arab tribes, the twelve princes of Ishmael, Keturah‘s descendants, and the dukes of Edom sprang from him. But it is to be more magnificently realized in a spiritual sense. “Nations” is a term usually applied, not to the chosen people, but to the other great branches of the human race. This points to the original promise, that in him should all the families of the earth be blessed. “Abraham.” The father of many nations is to be called by a new name, as he has come to have a new nature, and been elevated to a new dignity. The high father has become the father of the multitude of the faithful.
Genesis 17:7
Next, the spiritual part of the covenant comes into view. “To be a God unto thee, and to thy seed after thee.” Here we find God, in the progress of human development, for the third time laying the foundations of a covenant of grace with man. He dealt with Adam and with Noah, and now be deals with Abraham. “A perpetual covenant.” This covenant will not fail, since God has originated it, notwithstanding the moral instability of man. Though we cannot as yet see the possibility of fulfilling the condition on man‘s side, yet we may be assured that what God purposes will somehow be accomplished. The seed of Abraham will eventually embrace the whole human family in fellowship with God.
Genesis 17:8
Thirdly, the temporal and the spiritual are brought together. The land of promise is made sure to the heir of promise, “for a perpetual possession,” and God engages to “be their God.” The phrase “perpetual possession” has here two elements of meaning - first, that the possession, in its coming form of a certain land, shall last as long as the co-existing relations of things are continued; and, secondly, that the said possession in all the variety of its ever grander phases will last absolutely forever. Each form will be perfectly adequate to each stage of a progressive humanity. But in all its forms and at every stage it will be their chief glory that God is their God.
Genesis 17:9-14
The sign of the covenant. “And thou.” The other party to the covenant now learns his obligation. “Every male of you shall be circumcised.” Circumcision, as the rainbow, might have been in existence before it was adopted as the token of a covenant. The sign of the covenant with Noah was a purely natural phenomenon, and therefore entirely independent of man. That of the Abrahamic covenant was an artificial process, and therefore, though prescribed by God, was dependent on the voluntary agency of man. The former marked the sovereignty of God in ratifying the covenant and insuring its fulfillment, notwithstanding the mutability of man; the latter indicates the responsibility of man, the trust he places in the word of promise, and the assent he gives to the terms of the divine mercy. As the former covenant conveys a common natural blessing to all mankind and contemplates a common spiritual blessing, so the latter conveys a special spiritual blessing and contemplates its universal acceptance. The rainbow was the appropriate natural emblem of preservation from a flood; and the removal of the foreskin was the fit symbol of that removal of the old man and renewal of nature, which qualified Abraham to be the parent of a holy seed. And as the former sign foreshadows an incorruptible inheritance, so the latter prepares the way for a holy seed, by which the holiness and the heritage will at length be universally extended.
It is worthy of remark that in circumcision, after Abraham himself, the parent is the voluntary imponent, and the child merely the passive recipient of the sign of the covenant. Hereby is taught the lesson of parental responsibility and parental hope. This is the first formal step in a godly education, in which the parent acknowledges his obligation to perform all the rest. It is also, on the command of God, the formal admission of the believing parents‘ offspring into the privileges of the covenant, and therefore cheers the heart of the parent in entering upon the parental task. This admission cannot be reversed but by the deliberate rebellion of the child.
Still further, the sign of the covenant is to be applied to every male in the household of Abraham. This indicates that the servant or serf stands in the relation of a child to his master or owner, who is therefore accountable for the soul of his serf, as for that of his son. It points out the applicability of the covenant to others, as well as the children of Abraham, and therefore its capability of universal extension when the fulness of time should come. It also intimates the very plain but very often forgotten truth, that our obligation to obey God is not cancelled by our unwillingness. The serf is bound to have his child circumcised as long as God requires it, though he may be unwilling to comply with the divine commandments.
Genesis 17:12-14
The time of circumcision is the eighth day. Seven is the number of perfection. Seven days are therefore regarded as a type of perfectage and individuality. At this stage, accordingly, the sign of sanctification is made on the child, betokening the consecration of the heart to God, when its rational powers have come into noticeable activity. To be “cut off from his people” is to be excluded from any part in the covenant, and treated simply as a Gentile or alien, some of whom seem to have dwelt among the Israelites. It was sometimes accompanied with the sentence of death Exodus 31:14; and this shows that it did not of itself imply such a doom. Excommunication, however, for the omission of circumcision, would be extremely rare, as no parent would intentionally neglect the sacred interest of his child. Yet the omission of this rite has not been unprecedented, as the children of Israel did not generally circumcise their children in the wilderness Joshua 5:5.
Genesis 17:15-22
Sarai is now formally taken into the covenant, as she is to be the mother of the promised seed. Her name is therefore changed to Sarah, “princess.” Aptly is she so named, for she is to bear the child of promise, to become nations, and be the mother of kings. “Abraham fell upon his face and laughed.” From the reverential attitude assumed by Abraham we infer that his laughter sprang from joyful and grateful surprise. “Said in his heart.” The following questions of wonder are not addressed to God; they merely agitate the breast of the astonished patriarch. Hence, his irrepressible smile arises not from any doubt of the fulfillment of the promise, but from surprise at the unexpected mode in which it is to be fulfilled. Laughing in Scripture expresses joy in the countenance, as dancing does in the whole body.
Genesis 17:18-20
Abraham seems up to this time to have regarded Ishmael as the promised seed. Hence, a feeling of anxiety instantly penetrates his breast. It finds utterance in the prayer, “Oh that Ishmael might live before thee.” He asks “life” for his beloved son - that is, a share in the divine favor; and that “before God” - that is, a life of holiness and communion with God. But God asseverates his purpose of giving him a son by Sarah. This son is to be called Isaac - he that laughs or he shall laugh, in reference to the various emotions of surprise and delight with which his parents regarded his birth. Abram‘s prayer for Ishmael, however, is not unanswered. He is to be fruitful, beget twelve princes, and become a great nation. But Isaac is to be the heir of promise. At the present season next year he is to be born. The communication being completed, “God went” up from Abram.
Genesis 17:23-27
In the self-same day. - In this passage we have the prompt and punctual fulfillment of the command concerning circumcision detailed with all the minuteness due to its importance. Ishmael was thirteen years of age when he was circumcised. Josephus relates that the Arabs accordingly delay circumcision until the thirteenth year (Ant. I. 12. 2).
Concise Bible Commentary
Patriarchs and Prophets, 146-7
When Abraham was nearly one hundred years old, the promise of a son was repeated to him, with the assurance that the future heir should be the child of Sarah. But Abraham did not yet understand the promise. His mind at once turned to Ishmael, clinging to the belief that through him God's gracious purposes were to be accomplished. In his affection for his son he exclaimed, “O that Ishmael might live before Thee!” Again the promise was given, in words that could not be mistaken: “Sarah thy wife shall bear thee a son indeed; and thou shalt call his name Isaac: and I will establish My covenant with him.” Yet God was not unmindful of the father's prayer. “As for Ishmael,” He said, “I have heard thee: Behold, I have blessed him, ... and I will make him a great nation.” PP 146.1
The birth of Isaac, bringing, after a lifelong waiting, the fulfillment of their dearest hopes, filled the tents of Abraham and Sarah with gladness. But to Hagar this event was the overthrow of her fondly cherished ambitions. Ishmael, now a youth, had been regarded by all in the encampment as the heir of Abraham's wealth and the inheritor of the blessings promised to his descendants. Now he was suddenly set aside; and in their disappointment, mother and son hated the child of Sarah. The general rejoicing increased their jealousy, until Ishmael dared openly to mock the heir of God's promise. Sarah saw in Ishmael's turbulent disposition a perpetual source of discord, and she appealed to Abraham, urging that Hagar and Ishmael be sent away from the encampment. The patriarch was thrown into great distress. How could he banish Ishmael his son, still dearly beloved? In his perplexity he pleaded for divine guidance. The Lord, through a holy angel, directed him to grant Sarah's desire; his love for Ishmael or Hagar ought not to stand in the way, for only thus could he restore harmony and happiness to his family. And the angel gave him the consoling promise that though separated from his father's home, Ishmael should not be forsaken by God; his life should be preserved, and he should become the father of a great nation. Abraham obeyed the angel's word, but it was not without keen suffering. The father's heart was heavy with unspoken grief as he sent away Hagar and his son. PP 146.2
Read in context »Spiritual Gifts, vol. 3, 102-3
After the birth of Ishmael, the Lord manifested himself again to Abraham, and said unto him, “I will establish my covenant between me and thee, and thy seed after thee, in their generations, for an everlasting covenant.” Again the Lord repeated by his angel his promise to give Sarah a son, and that she should be a mother of many nations. Abraham did not yet understand the promise of God. His mind immediately rests upon Ishmael, as though through him would come the many nations promised, and he exclaims, in his affection for his son, “Oh, that Ishmael might live before thee.” 3SG 102.1
Read in context »The Story of Redemption, 78-81
Abraham was also compelled to listen to Hagar's complaints of abuse from Sarah. Abraham is in perplexity. If he seeks to redress the wrongs of Hagar he increases the jealousy and unhappiness of Sarah, his first and much-loved wife. Hagar flees from the face of Sarah. An angel of God meets her and comforts her and also reproves her for her haughty conduct, in bidding her return to her mistress and submit herself under her hands. SR 78.1
After the birth of Ishmael the Lord manifested Himself again to Abraham and said unto him, “I will establish My covenant between Me and thee and thy seed after thee in their generations for an everlasting covenant.” Again the Lord repeated by His angel His promise to give Sarah a son, and that she should be a mother of many nations. Abraham did not yet understand the promise of God. His mind immediately rested upon Ishmael, as though through him would come the many nations promised, and he exclaimed, in his affection for his son, “O that Ishmael might live before Thee!” SR 78.2
Again the promise is more definitely repeated to Abraham: “Sarah thy wife shall bear thee a son indeed; and thou shalt call his name Isaac: and I will establish My covenant with him for an everlasting covenant, and with his seed after him.” Angels are sent the second time to Abraham on their way to destroy Sodom, and they repeat the promise more distinctly that Sarah shall have a son. SR 78.3
Read in context »