Genesis 11:28
Notes on the Whole Bible
- Section X - Abraham
- XXXVI. The Father of Abram
27. לוט lôṭ Lot, “veil;” verb: “cover.”
28. אוּר 'ûr Ur, “light, flame.” כשׂדים kaśdı̂ym Kasdim, Cardi, Kurds, Χαλδαῖοι Kaldaioi כסד kesed “gain?” Arabic. Ur Kasdim has been identified with Hur, now called Mugheir (the bitumened), a heap of ruins lying south of the Euphrates, nearly opposite its jucnction with the Shat el-Hie. Others place it at Edessa, now Orfa, a short way north of Carrhae.
29. שׂרי sāray Sarai, “strife;” שׂרה śārâh “strive, rule.” מלכה mı̂lkâh Milkah, “counsel, queen;” verb: “counsel, reign.” יסכה yı̂sekâh Jiskah, “one who spies, looks out.”
31. הרן hārān Haran, “burnt place.” Χαῤῥαι Charran Κάῤῥαι Karrai a town on the Bilichus (Bililk), a tributary of the Frat, still called Harran. This has been identified by some with Harae, on the other side of the Frat, not far from Tadmor or Palmyra.
This passage forms the commencement of the sixth document, as is indicated by the customary phrase, “These are the generations.” The sense also clearly accords with this distinction; and it accounts for the repetition of the statement, “Terah begat Abram, Nahor, and Haran.” Yet the scribe who finally arranged the text makes no account of this division; as he inserts neither the Hebrew letter פ (p ) nor even the Hebrew letter ס (s ) at its commencement, while he places the threefold פ (p ), marking the end of a Sabbath lesson, at its close. We learn from this that the Jewish rabbis did not regard the opening phrase as a decided mark of a new beginning, or any indication of a new author. Nevertheless, this passage and the preceding one form the meet prelude to the history of Abram - the one tracing his genealogy from Shem and Heber, and the other detailing his relations with the family out of which he was called.
God has not forsaken the fallen race. On the contrary, he has once and again held out to them a general invitation to return, with a promise of pardon and acceptance. Many of the descendants of Noah have already forsaken him, and he foresees that all, if left to themselves, will sink into ungodliness. Notwithstanding all this, he calmly and resolutely proceeds with his purpose of mercy. In the accomplishment of this eternal purpose he moves with all the solemn grandeur of longsuffering patience. One day is with him as a thousand years, and a thousand years as one day. Out of Adam‘s three sons he selects one to be the progenitor of the seed of the woman; out of Noah‘s three sons he again selects one; and now out of Terah‘s three is one to be selected. Among the children of this one he will choose a second one, and among his a third one before he reaches the holy family. Doubtless this gradual mode of proceeding is in keeping with the hereditary training of the holy nation, and the due adjustment of all the divine measures for at length bringing the fullness of the Gentiles into the covenant of everlasting peace.
The history here given of the postdiluvians has a striking resemblance in structure to that of the antediluvians. The preservation of Noah from the waters of the flood, is the counterpart of the creation of Adam after the land had risen out of the roaring deep. The intoxication of Noah by the fruit of a tree corresponds with the fall of Adam by eating the fruit of a forbidden tree. The worldly policy of Nimrod and his builders is parallel with the city-building and many inventions of the Cainites. The pedigree of Abram the tenth from Shem, stands over against the pedigree of Noah the tenth from Adam; and the paragraph now before us bears some resemblance to what precedes the personal history of Noah. All this tends to strengthen the impression made by some other phenomena, already noticed, that the book of Genesis is the work of one author, and not a mere file of documents by different writers.
The present paragraph is of special interest for the coming history. Its opening word and intimates its close connection with the preceding document; and accordingly we observe that the one is merely introductory to the other. The various characters brought forward are all of moment. Terah is the patriarch and leader of the migration for part of the way. Abram is the subject of the following narrative. Nahor is the grandfathcr of Rebekah. Haran is the father of Lot the companion of Abram, of Milcah the wife of Nahor and grandmother of Rebekah, and of Iskah. Iskah alone seems to have no connection with the subsequent narrative. Josephus says Sarai and Milkah were the daughters of Haran, taking no notice of Iskah. He seems, therefore, to identify Sarai and Iskah. Jerome, after his Jewish teachers, does the same. Abram says of Sarai, “She is the daughter of my father, but not the daughter of my mother” Genesis 20:12.
In Hebrew phrase the granddaughter is termed a daughter; and therefore this statement might be satisfied by her being the daughter of Haran. Lot is called the brother‘s son and the brother of Abram Genesis 14:12, Genesis 14:16. If Sarai be Haran‘s daughter, Lot is Abram‘s brother-in-law. This identification would also explain the introduction of Iskah into the present passage. Still it must be admitted, on the other hand, that persons are sometimes incidentally introduced in a history of facts, without any express connection with the course of the narrative, as Naamah in the history of the Cainites. The studied silence of the sacred writer in regard to the parentage of Sarai, in the present connection, tells rather in favor of her being the actual daughter of Terah by another wife, and so strictly the half-sister of Abram. For the Mosaic law afterward expressly prohibited marriage with “the daughter of a father” Leviticus 18:9. And, lastly, the text does not state of Iskah, “This is Sarai,” which would accord with the manner of the sacred writer, and is actually done in the Targum of Pseudo-Jonathan.
Genesis 11:28
And Haran died in the presence of his father Terah. - There is reason to believe that Haran was the oldest son of Terah. Though mentioned in the third place, like Japheth the oldest son of Noah, yet, like Japheth, also, his descendants are recounted first. He is the father of Lot, Milkah, and Iskah. His brother Nahor marries his daughter Milkah. If Iskah be the same as Sarai, Haran her father must have been some years older than Abram, as Abram was only ten years older than Sarai; and hence her father, if younger than Abram, must have been only eight or nine when she was born, which is impossible. Hence, those who take Iskah to be Sarai, must regard Abram as younger than Haran.
In the land of his birth. - The migration of Terah, therefore, did not take place until after the death of Haran. At all events, his three grandchildren, Lot, Milkah, and Iskah, were born before he commenced his journey. Still further, Milkah was married to Nahor for some time before that event. Hence, allowing thirty years for a generation, we have a period of sixty years and upwards from the birth of Haran to the marriage of his daughter. But if we take seventy years for a generation, which is far below the average of the Samaritan or the Septuagint, we have one hundred and forty years, which will carry us beyond the death of Terah, whether we reckon his age at one hundred and forty-five with the Samaritan, or at two hundred and five with the other texts. This gives another presumption in favor of the Hebrew average for a generation.
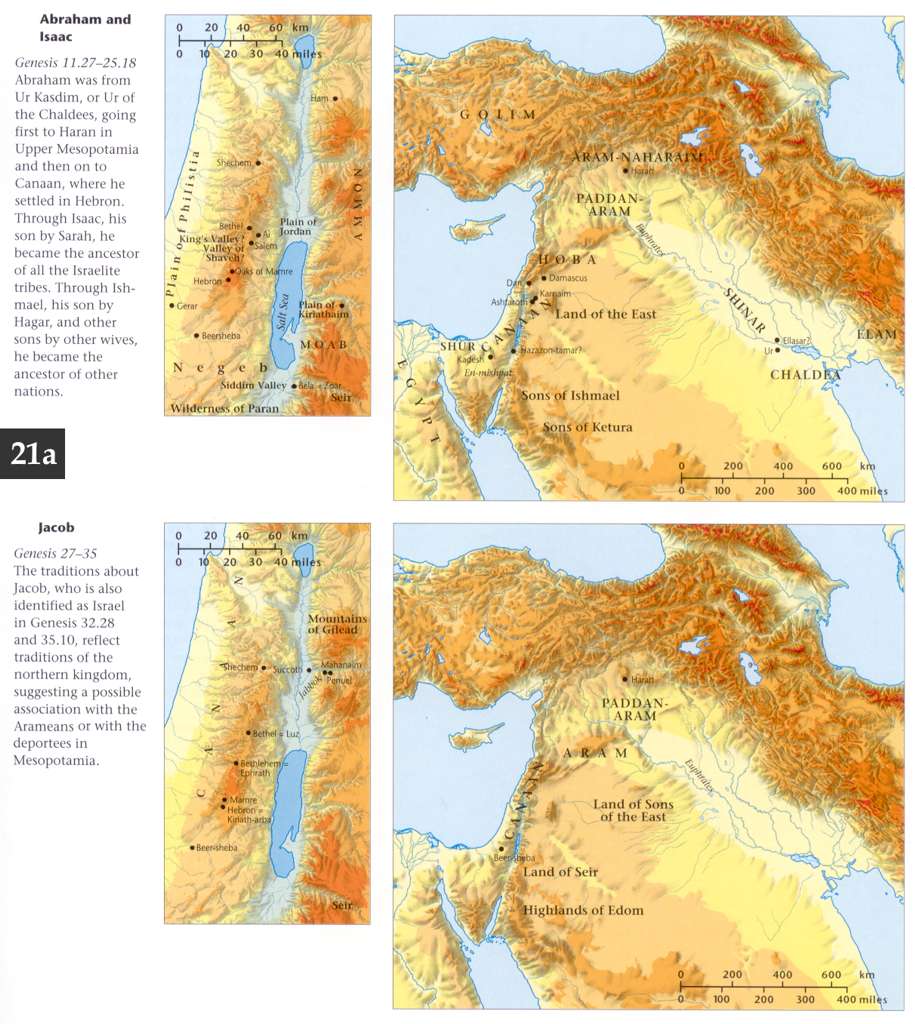
In Ur of the Kasdim. - The Kasdim, Cardi, Kurds, or Chaldees are not to be found in the table of nations. They have been generally supposed to be Shemites. This is favored by the residence of Abram among them, by the name Kesed, being a family name among his kindred Genesis 22:22, and by the language commonly called Chaldee, which is a species of Aramaic. But among the settlers of the country, the descendants of Ham probably prevailed in early times. Nimrod, the founder of the Babylonian Empire, was a Kushite. The ancient Babylonish language, Rawlinson (Chaldaea) finds to be a special dialect, having affinities with the Shemitic, Arian, Turanian, and Hamitic tongues. The Chaldees were spread over a great extent of surface; but their most celebrated seat was Chaldaea proper, or the land of Shinar. The inhabitants of this country seem to have been of mixed descent, being bound together by political rather than family ties.
Nimrod, their center of union, was a despot rather than a patriarch. The tongue of the Kaldees, whether pure or mixed, and whether Shemitic or not, is possibly distinct from the Aramaic, in which they addressed Nebuchadnezzar in the time of Daniel Daniel 1:4; Daniel 2:4. The Kaldin at length lost their nationality, and merged into the caste or class of learned men or astrologers, into which a man might be admitted, not merely by being a Kaldai by birth, but by acquiring the language and learning of the Kasdim Daniel 1:4; Daniel 5:11. The seats of Chaldee learning were Borsippa (Birs Nimrud), Ur, Babylon, and Sepharvaim (Sippara, Mosaib). Ur or Hur has been found by antiquarian research (see Rawlinson‘s Ancient Monarchies) in the heap of ruins called Mugheir, “the bitumened.” This site lies now on the right side of the Frat; but the territory to which it belongs is mainly on the left. And Abram coming from it would naturally cross into Mesopotamia on his way to Haran. Orfa, the other supposed site of Ur, seems to be too near Haran. It is not above twenty or twenty-five miles distant, which would not be more than one day‘s journey.
Genesis 11:29, Genesis 11:30
But Sarai was barren. - From this statement it is evident that Abram had been married for some time before the migration took place. It is also probable that Milkah had begun to have a family; a circumstance which would render the barrenness of Sarai the more remarkable.
Genesis 11:31, Genesis 11:32
And Terah took Abram. - Terah takes the lead in this emigration, as the patriarch of the family. In the Samaritan Pentateuch Milkah is mentioned among the emigrants; and it is not improbable that Nahor and his family accompanied Terah, as we find them afterward at Haran, or the city of Nahor Genesis 24:10. “And they went forth with them.” Terah and Abram went forth with Lot and the other companions of their journey. “To go into the land of Kenaan. It was the design of Terah himself to settle in the land of Kenaan. The boundaries of this land are given in the table of nations Genesis 10:19. The Kenaanites were therefore in possession of it when the table of nations was drawn up. It is certain, however, that there were other inhabitants, some of them Shemites probably, anterior to Kenaan, and subjected by his invading race. The prime motive to this change of abode was the call to Abram recorded in the next chapter. Moved by the call of God, Abram “obeyed; and he went out not knowing whither he went” Hebrews 11:8.
But Terah was influenced by other motives to put himself at the head of this movement. The death of Haran, his oldest son, loosened his attachment to the land of his birth. Besides, Abram and Sarai were no doubt especially dear to him, and he did not wish to lose their society. The inhabitants also of Ur had fallen into polytheism, or, if we may so speak, allotheism, the worship of other gods. Terah had himself been betrayed into compliance with this form of impiety. It is probable that the revelation Abram had received from heaven was the means of removing this cloud from his mind, and restoring in him the knowledge and worship of the true God. Hence, his desire to keep up his connection with Abram, who was called of God. Prayerful conversation with the true and living God, also, while it was fast waning in the land of the Kasdim, seems to have been still maintained in its ancient purity in some parts of the land of Kenaan and the adjacent countries. In the land of Uz, a Shemite, perhaps even at a later period, lived Job; and in the neighboring districts of Arabia were his several friends, all of whom acknowledged the true God. And in the land of Kenaan was Melkizedec, the king of Salem, and the priest of the Most High God. A priest implies a considerable body of true worshippers scattered over the country. Accordingly, the name of the true God was known and revered, at least in outward form, wherever Abram went, throughout the land. The report of this comparatively favorable state of things in the land of Kenaan would be an additional incentive to the newly enlightened family of Terah to accompany Abram in obedience to the divine call.
Terah set out on his journey, no doubt, as soon after the call of Abram as the preparatory arrangements could be made. Now the promise to Abram was four hundred and thirty years before the exodus of the children of Israel out of Egypt Exodus 12:40. Of this long period his seed was to be a stranger in a land that was not theirs for four hundred years Genesis 15:13. Hence, it follows that Isaac, his seed, was born thirty years after the call of Abram. Now Abram was one hundred years old when Isaac was born, and consequently the call was given when he was seventy years of age - about five years before he entered the land of Kenaan Genesis 12:4. This whole calculation exactly agrees with the incidental statement of Paul to the Galatians Galatians 3:17 that the law was four hundred and thirty years after the covenant of promise. Terah was accordingly two hundred years old when he undertook the long journey to the land of Kenaan; for he died at two hundred and five, when Abram was seventy-five. Though proceeding by easy stages, the aged patriarch seems to have been exhausted by the length and the difficulty of the way. “They came to Haran and dwelt there.” Broken down with fatigue, he halts for a season at Haran to recruit his wasted powers. Filial piety, no doubt, kept Abram watching over the last days of his venerable parents, who probably still cling to the fond hope of reaching the land of his adoption. Hence, they all abode in Haran for the remainder of the five years from the date of Abram‘s call to leave his native land. “And Terah died in Haran.” This intimates that he would have proceeded with the others to the land of Kenaan if his life had been prolonged, and likewise that they did not leave Haran until his death.
We have already seen that Abram was seventy-five years of age at the death of Terah. It follows that he was born when Terah was one hundred and thirty years old, and consequently sixty years after Haran. This is the reason why we have placed one hundred and thirty (seventy and sixty), in the genealogical table opposite Terah, because the line of descent is not traced through Haran, who was born when he was seventy, but through Abram, who by plain inference was born when he was one hundred and thirty years old. It will be observed, also, that we have set down seventy opposite Abram as the date of his call, from which is counted the definite period of four hundred and thirty years to the exodus. And as all our texts agree in the numbers here involved, it is obvious that the same adjustment of years has in this case to be made, whatever system of chronology is adopted. Hence, Abram is placed first in the list of Terah‘s sons, simply on account of his personal pre-eminence as the father of the faithful and the ancestor of the promised seed; he and his brother Nahor are both much younger than Haran, are married only after his death, and one of them to his grown-up daughter Milkah; and he and his nephew Lot are meet companions in age as well as in spirit.
Hence, also, Abram lingers in Haran, waiting to take his father with him to the land of promise, if he should revive so far as to be fit for the journey. But it was not the lot of Terah to enter the land, where he would only have been a stranger. He is removed to the better country, and by his departure contributes no doubt to deepen the faith of his son Abram, of his grandson Lot, and of his daughter-in-law Sarai. This explanation of the order of events is confirmed by the statement of Stephen: “The God of glory appeared unto our father Abraham when he was in Mesopotamia, before he dwelt in Charran. Then came he out of the land of the Chaldeans and dwelt in Charran; and from thence, when his father was dead, he removed him into this land, wherein ye now dwell” Acts 7:2-4.
Concise Bible Commentary
Counsels on Diet and Foods, 117
194. Man came from the hand of his Creator perfect in organization and beautiful in form. The fact that he has for six thousand years withstood the ever-increasing weight of disease and crime is conclusive proof of the power of endurance with which he was first endowed. And although the antediluvians generally gave themselves up to sin without restraint, it was more than two thousand years before the violation of natural law was sensibly felt. Had Adam originally possessed no greater physical power than men now have, the race would ere this have become extinct. CD 117.1
Through the successive generations since the fall, the tendency has been continually downward. Disease has been transmitted from parents to children, generation after generation. Even infants in the cradle suffer from afflictions caused by the sins of their parents. CD 117.2
Moses, the first historian, gives quite a definite account of social and individual life in the early days of the world's history, but we find no record that an infant was born blind, deaf, crippled, or imbecile. Not an instance is recorded of a natural death in infancy, childhood, or early manhood. Obituary notices in the book of Genesis run thus: “And all the days that Adam lived were nine hundred and thirty years; and he died.” “And all the days of Seth were nine hundred and twelve years; and he died.” Concerning others the record states, “He died in a good old age, an old man, and full of years.” It was so rare for a son to die before his father, that such an occurrence was considered worthy of record: “Haran died before his father Terah.” The patriarchs from Adam to Noah, with few exceptions, lived nearly a thousand years. Since then the average length of life has been decreasing. CD 117.3
At the time of Christ's first advent, the race had already so degenerated that not only the old, but the middle-aged and the young, were brought from every city to the Saviour, to be healed of their diseases. Many labored under a weight of misery inexpressible. CD 117.4
Read in context »Spiritual Gifts, vol. 4a, 121
The people who lived before the flood ate animal food, and gratified their lusts until their cup of iniquity was full, and God cleansed the earth of its moral pollution by a flood. Then the third dreadful curse rested upon the earth. The first curse was pronounced upon the posterity of Adam and upon the earth, because of disobedience. The second curse came upon the ground after Cain slew his brother Abel. The third most dreadful curse from God, came upon the earth at the flood. 4aSG 121.1
After the flood the people ate largely of animal food. God saw that the ways of man were corrupt, and that he was disposed to exalt himself proudly against his Creator, and to follow the inclinations of his own heart. And he permitted that long-lived race to eat animal food to shorten their sinful lives. Soon after the flood the race began to rapidly decrease in size, and in length of years. There were a class of very large animals which perished at the flood. God knew that the strength of man would decrease, and these mammoth animals could not be controlled by feeble man. 4aSG 121.2
Sin has prevailed since the fall. While a few have remained faithful to God, the great majority have corrupted their ways before him. The destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah was on account of their great wickedness. They gave loose rein to their intemperate appetites, then to their corrupt passions, until they were so debased, and their sins were so abominable, that their cup of iniquity was full, and they were consumed with fire from heaven. 4aSG 121.3
When the Lord brought his people from Egyptian bondage, he led them through the wilderness to prove them, and try them. He promised to be their God, and to take them to himself as his peculiar treasure. He did not prohibit their eating meat, but withheld it from them in a great measure. He gave them food which he designed that they should have, which was healthy, and of which they could eat freely. He rained their bread from Heaven, and gave them purest water out of the flinty rock. He made a covenant with them, that if they would obey him in all things, he would put no disease upon them. But the Israelites were not satisfied with the food which God gave them. They murmured against Moses and against God, and wished themselves back in Egypt, where they could sit by the flesh pots. God in his anger gave them flesh to gratify their lustful appetite, and great numbers of them died in the act of eating the meat for which they had lusted. While it was yet between their teeth the curse of God came upon them. God here teaches his people that he is displeased with their permitting their appetite to control them. The Israelites at times would prefer slavery, and even death, rather than to be deprived of meat. 4aSG 121.4
Read in context »Testimonies for the Church, vol. 4, 29
Christ paid a dear price for man's redemption. In the wilderness of temptation He suffered the keenest pangs of hunger; and while He was emaciated with fasting, Satan was at hand with his manifold temptations to assail the Son of God, to take advantage of His weakness and overcome Him, and thus thwart the plan of salvation. But Christ was steadfast. He overcame in behalf of the race, that He might rescue them from the degradation of the Fall. Christ's experience is for our benefit. His example in overcoming appetite points out the way for those who would be His followers and finally sit with Him on His throne. 4T 29.1
Christ suffered hunger in the fullest sense. Mankind generally have all that is needful to sustain life. And yet, like our first parents, they desire that which God would withhold because it is not best for them. Christ suffered hunger for necessary food and resisted the temptation of Satan upon the point of appetite. Indulgence of intemperate appetite creates in fallen man unnatural desires for the things which will eventually prove his ruin. 4T 29.2
Man came from the hand of God perfect in every faculty of mind and body; in perfect soundness, therefore in perfect health. It took more than two thousand years of indulgence of appetite and lustful passions to create such a state of things in the human organism as would lessen vital force. Through successive generations the tendency was more swiftly downward. Indulgence of appetite and passion combined led to excess and violence; debauchery and abominations of every kind weakened the energies and brought upon the race diseases of every type, until the vigor and glory of the first generations passed away, and, in the third generation from Adam, man began to show signs of decay. Successive generations after the Flood degenerated more rapidly. 4T 29.3
Read in context »Patriarchs and Prophets, 127
The call from heaven first came to Abraham while he dwelt in “Ur of the Chaldees” and in obedience to it he removed to Haran. Thus far his father's family accompanied him, for with their idolatry they united the worship of the true God. Here Abraham remained till the death of Terah. But from his father's grave the divine Voice bade him go forward. His brother Nahor with his household clung to their home and their idols. Besides Sarah, the wife of Abraham, only Lot, the son of Haran long since dead, chose to share the patriarch's, pilgrim life. Yet it was a large company that set out from Mesopotamia. Abraham already possessed extensive flocks and herds, the riches of the East, and he was surrounded by a numerous body of servants and retainers. He was departing from the land of his fathers, never to return, and he took with him all that he had, “their substance that they had gathered, and the souls that they had gotten in Haran.” Among these were many led by higher considerations than those of service and self-interest. During their stay in Haran, both Abraham and Sarah had led others to the worship and service of the true God. These attached themselves to the patriarch's household, and accompanied him to the land of promise. “And they went forth to go into the land of Canaan; and into the land of Canaan they came.” PP 127.1
The place where they first tarried was Shechem. Under the shade of the oaks of Moreh, in a wide, grassy valley, with its olive groves and gushing springs, between Mount Ebal on the one side and Mount Gerizim on the other, Abraham made his encampment. It was a fair and goodly country that the patriarch had entered—“a land of brooks of water, of fountains and depths that spring out of valleys and hills; a land of wheat, and barley, and vines, and fig trees, and pomegranates; a land of oil olive, and honey.” Deuteronomy 8:7, 8. But to the worshiper of Jehovah, a heavy shadow rested upon wooded hill and fruitful plain. “The Canaanite was then in the land.” Abraham had reached the goal of his hopes to find a country occupied by an alien race and overspread with idolatry. In the groves were set up the altars of false gods, and human sacrifices were offered upon the neighboring heights. While he clung to the divine promise, it was not without distressful forebodings that he pitched his tent. Then “the Lord appeared unto Abram, and said, Unto thy seed will I give this land.” His faith was strengthened by this assurance that the divine presence was with him, that he was not left to the mercy of the wicked. “And there builded he an altar unto the Lord, who appeared unto him.” Still a wayfarer, he soon removed to a spot near Bethel, and again erected an altar, and called upon the name of the Lord. PP 127.2
Read in context »Testimonies for the Church, vol. 3, 138
The book of Genesis gives quite a definite account of social and individual life, and yet we have no record of an infant's being born blind, deaf, crippled, deformed, or imbecile. There is not an instance upon record of a natural death in infancy, childhood, or early manhood. There is no account of men and women dying of disease. Obituary notices in the book of Genesis run thus: “And all the days that Adam lived were nine hundred and thirty years: and he died.” “And all the days of Seth were nine hundred and twelve years: and he died.” Concerning others, the record states: He lived to a good old age; and he died. It was so rare for a son to die before the father that such an occurrence was considered worthy of record: “And Haran died before his father Terah.” Haran was a father of children before his death. 3T 138.1
God endowed man with so great vital force that he has withstood the accumulation of disease brought upon the race in consequence of perverted habits, and has continued for six thousand years. This fact of itself is enough to evidence to us the strength and electrical energy that God gave to man at his creation. It took more than two thousand years of crime and indulgence of base passions to bring bodily disease upon the race to any great extent. If Adam, at his creation, had not been endowed with twenty times as much vital force as men now have, the race, with their present habits of living in violation of natural law, would have become extinct. At the time of Christ's first advent the race had degenerated so rapidly that an accumulation of disease pressed upon that generation, bringing in a tide of woe and a weight of misery inexpressible. 3T 138.2
Read in context »