1 Kings 6:36
Bible Commentary
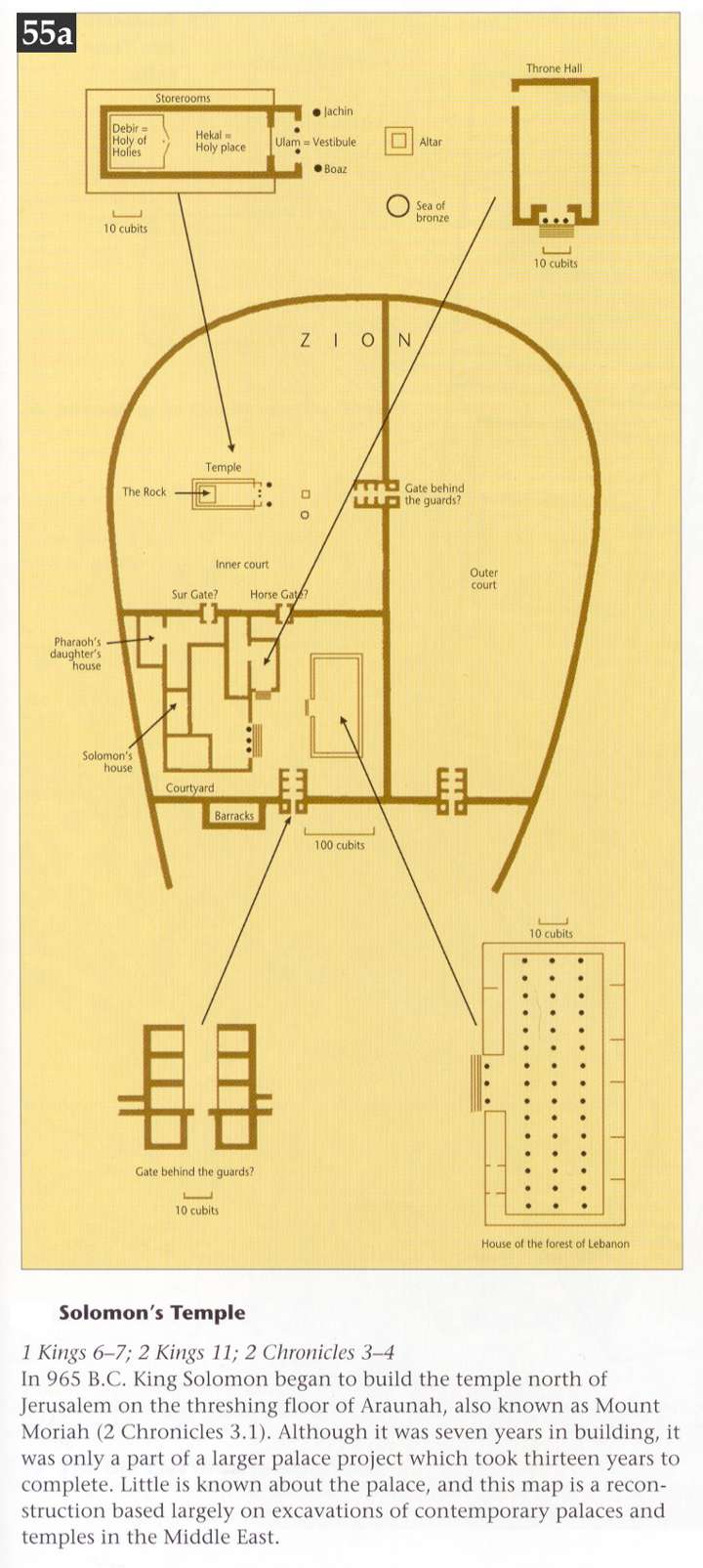
Three rows of hewed stone, and a row of cedar beams - Does not this intimate that there were three courses of stone, and then one course of timber all through this wall? Three strata of stone and one stratum of timber, and so on. If so, could such a building be very durable? This is also referred to in the succeeding chapter, 1 Kings 7:11; and as both the temple and Solomon's house were built in the same manner, we may suppose that this was the ordinary way in which the better sort of buildings were constructed. Calmet thinks that to this mode of building the prophet alludes, Habakkuk 2:11; : The stone shall cry out of the wall, and the beam out of the timber shall answer it. But it should be observed that this was in the inner court, and therefore the timber was not exposed to the weather. The outer court does not appear to have been built stratum super stratum of stone and wood.
Notes on the Whole Bible
The inner court - An outer court is mentioned in 2 Chronicles 4:9. The inner court is probably identical with the “higher court” of Jeremiah Jeremiah 36:10, being raised above the outer, as were sometimes the inner courts of Assyrian palaces. The court seems to have surrounded the temple. Its dimensions may be reasonably presumed to have been double those of the court of the tabernacle, i. e., 100 cubits on each side of the temple, and 200 cubits at the ends; or, about 720 feet long by 360 broad.
With three rows of hewed stone - Either a fence enclosing the court, or the area of the court, which was possibly formed by three layers of hewn stone placed one above the other, and was then boarded on the top with cedar planks. Such a construction would no doubt be elaborate; but if it was desired to elevate the inner court above the outer, this is the way in which it would be likely to have been done. The temple would be placed, like the Assyrian palaces, on an artificial platform; and the platform, being regarded as a part of the sacred building, would be constructed of the best material.
Concise Bible Commentary