Numbers 21:35
Bible Commentary
So they smote him, and his sons - There is a curious note of Dr. Lightfoot here, of which I should think it wrong to deprive the reader.
"Sihon and Og conquered, A. M. 2553. Of the life of Moses, 120. From the Exodus, 40. It is now six and twenty generations from the creation, or from Adam to Moses; and accordingly doth Psalm 136, rehearse the durableness of God's mercy six and twenty times over, beginning the story with the creation, and ending it in the conquest of Sihon and Og. The numerals of the name יהוה Jehovah amount to the sum of six and twenty."
On some difficulties in this chapter Dr. Kennicott makes the following observations: -
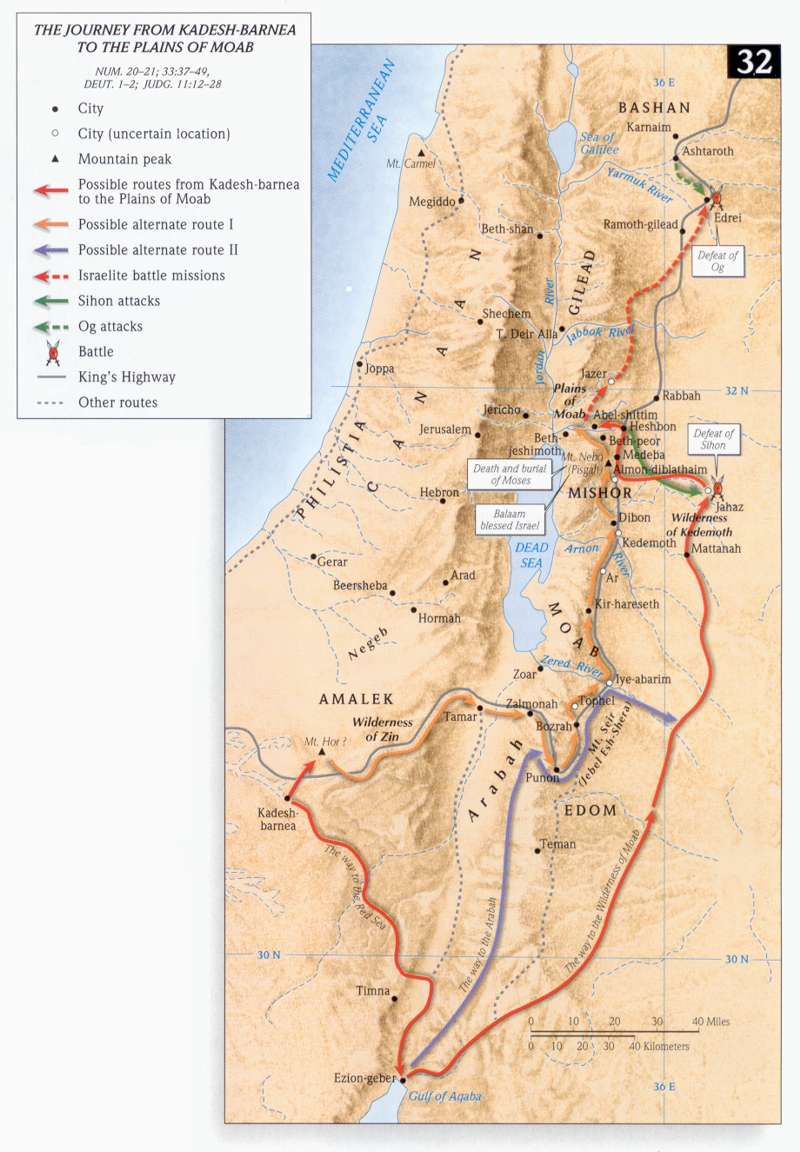
"This one chapter has several very considerable difficulties; and some verses, as now translated, are remarkably unintelligible, A true state of this chapter is not, however, to be despaired of; and it has in it some circumstances which merit more than common attention. It contains the history of the last part of the travels of the Israelites in their way to the promised land; beginning with them at Mount Hor, the thirty-fourth encampment, and concluding with them, as in their forty-second and last encampment, near Jordan, in the country which they had acquired by conquest over Sihon, king of the Amorites.
"It begins with saying - that King Arad, the Canaanite, who dwelt in the south, (in the land of Canaan, Numbers 33:40;), attacked Israel and was defeated, and that Israel destroyed their cities; and that, after destroying these Canaanite cities, and consequently after being in a part of Canaan, a part of the very country they were going to, on the west of the Dead Sea, they returned towards the Red Sea, and near the eastern tongue or gulf of the Red Sea, on the south of Edom, marched round Edom to the east of the Dead Sea, in order to enter Canaan from the east side of Jordan!
"This surprising representation of so vast and dangerous a march, quite unnecessarily performed, is owing to two circumstances. The first is, ( Numbers 21:1;), the Canaanites heard that Israel was coming by the way of the spies, meaning, by the way the spies went from Kadesh-Barnea into Canaan. But this being impossible, because Israel had now marched from Meribah-Kadesh to Mount Hor, beyond Ezion-gaber, and were turning round Edom, to the south-east; it is happy that the word rendered spies, in our version, is in the Greek a proper name, (Atharim), which removes that difficulty: and the other difficulty ( Numbers 21:2, Numbers 21:3;) is removed by the Greek version likewise, according to which, the vow made, with the facts subsequent, does not signify destroying the Canaanite cities, but devoting them to destruction at some future time. See Wall's Crit. Notes.
"It proceeds with saying, that after defeating the Canaanites at Mount Hor, they journeyed from Mount Hor by the way of the Red Sea, (in the road from Ammon, Midian, etc., to the eastern gulf of the Red Sea), to compass the land of Edom; that on their murmuring for want both of bread and of water they were punished by fiery serpents, after which they marched to Oboth, and thence to Ije-abarim in the wilderness, east of Moab. The encampments of the Israelites, amounting to forty-two, are recorded all together, in historical succession, in Numbers 33, where Ije-abarim is the 38th; Dibon-gad, 39; Almon-Diblathaim, 40; mountains of Abarim, 41; and the plains of Moab, by Jordan, 42. This regular detail in Numbers 33 has occasioned great perplexity as to Numbers 21, where, after the stations at Oboth and Ije-abarim, in Numbers 21:10, Numbers 21:11, we have, in Numbers 21:19, Numbers 21:20, the words Mattanah, Nahaliel, and Bamoth; which are usually considered as the proper names of three places, but widely different from the three proper names after Ije-abarim in the catalogue at Numbers 33.
"But there is, in reality, no inconsistency here. In the plain and historical catalogue (Numbers 33). the words are strictly the proper names of the three places; but here the words Mattanah, Nahaliel, and Bamoth follow some lines of poetry, and seem to form a continuation of the song. They evidently express figurative and poetical ideas. The verbs journeyed from and pitched in are not found here, though necessary to prose narration: see Numbers 33:10; and Numbers 33:11; here, and Numbers 33. Lastly, Numbers 21:20, (in this 21st chapter), usually supposed to express the last encampment, does not. Pisgah signifies a hill; and the Israelites could not encamp on the top of any single hill, such as this is described. Balak took Balaam to the top of Peor, which looketh toward Jeshimon, ( Numbers 23:28;), which Peor undoubtedly was in Moab. He took him to another hill in Moab, when he took him ( Numbers 23:14;) to the top of Pisgah, in the field of Zophim. And if the Pisgah or hill in Numbers 21:20, was in the country of Balak, it could not point out the last encampment, which was not in Balak's country, but north of Arnon.
"The word Mattanah probably alludes to a place distinguished by some gift or blessing from God. Fagius says:
Nomen loci, ab eventu aquarum quas Dominus ibi dedit, sic appellati; מתנה nam significat donum-
'The name of the place was so called, from the circumstance of the waters which the Lord gave there; for Mattanah signifies a gift.' נהליאל Nahaliel is torrentes Dei; i. e., great streams, particularly seasonable or salutary. And במות Bamoth ( Numbers 21:20;) may point out any high places of signal benefit in the country of Moab, or it may answer to the last station but one, which was the mountains of Abarim.
If, therefore, these words were meant to express poetically some eminent blessing, what blessing was so likely to be then celebrated as copious streams of water? And after they had wandered nearly forty years through many a barren desert, and after (compare Deuteronomy 8:15;) having passed through that great and terrible wilderness, wherein were fiery serpents and drought, where there was no water, it is no wonder they should shout for joy at finding water in plenty, and finding it almost on the banks of Arnon, the last river they were to pass, in their way to their last station, east of Jordan. No wonder they should sing in poetic rapture, that after the wilderness was (Mattanah) the Gift Of God; meaning the great well in Moab, dug by public authority; and no wonder that, after such a gift, there were (Nahaliel) blessed streams, by which they passed, till they came to (Bamoth) the high places from which, perhaps, these streams descended. And the thanksgiving ends, where the blessing was no longer wanted, on their coming down into the valley, along the banks of Arnon, which was then the north boundary of Moab.
"The Israelites had spent no less than thirty-eight years in coming from Kadesh-Barnea to their encampment north of Zared. Here, at this fortieth station, they were commanded to pass through Moab by ער Ar, the chief city; but were not to stop till they came to the valley on the south of Arnon. At this last station but one they probably continued no longer than was necessary for sending messengers to Sihon, king of the Amorites, at Heshbon, and receiving his answer. They then crossed the Arnon; and having vanquished Sihon and Og, took possession of the forty-second and last encampment.
"This one chapter has three pieces of poetry, either fragments or complete; and poetry, seldom found in a historical narrative, may be here accounted for from the exuberance of joy which must have affected these wearied travelers, when arriving thus happily near their journey's end. What occurs first is in Numbers 21:14; and has often been called the fragment of an old Amorite song. But it may have been Amorite or Moabite, or either or neither, for the subject matter of it, as it is generally understood, if indeed it can be said to be understood at all. The words ארנו הנתליס ואת בסופה והב את , usually supposed to contain this fragment, do not signify, as in our English version, What he did in the Red Sea, and in the brooks of Arnon. Without enumerating the many interpretations given by others, I shall offer a new one, which seems to make good sense, and a sense very pertinent.
"Observe first, that there must have been a place called Suph, near the conflux of the Arnon and Jordan; because Moses, whilst in that last station, begins Deuteronomy with saying, he was on this side (i. e., east) of Jordan, over against Suph. By this word is not here meant the Red Sea; partly, because that has every where else the word for sea before it, and partly, because of the great distance of the Red Sea now from Moses. The single word, therefore, signifies here some place in itself obscure, because no where mentioned but in these two passages. And yet we cannot wonder that Moses should mention it twice, as the word Suph, introduced in speaking of the two last encampments, recalled to mind the Sea of Suph, so glorious to Israel, near the beginning of their march towards Canaan.
"Moses had now led Israel from the Red Sea to the river Arnon, through many dreadful dangers, partly from hostile nations, partly from themselves; such dangers as no other people ever experienced, and such as no people could have surmounted, without the signal favor of the Almighty. And here, just before the battles with Sihon and Og, he reminds them of Pharaoh, etc.; and he asserts, that in the history of the wars it shall be recorded that Jehovah, who had triumphantly brought Israel through the Sea of Suph, near Egypt, at first, had now conducted him to Suph, near Arnon; that
Jehovah went with him to Suph,
And he came to the streams of Arnon.
"This version removes the difficulties urged by Hobbes, page 266, fol. 1750; by Spinoza, page 108, 4th., 1670; and retailed in a deistical pamphlet called The Doubts of the Infidels, page 4, 8vo., 1781.
"The general meaning of the next piece of poetry seems to be this: that at some distance from the city of Ar, by which the Israelites were to pass, ( Deuteronomy 2:18;), they came to A Well of uncommon size and magnificence, which seems to have been sought out, built up, and adorned for the public, by the rulers of Moab. And it is no wonder that, on their arrival at such a well, they should look upon it as a blessing from Heaven, and speak of it as a new miracle in their favor.
- Then Israel sang this song: - Spring up, O Well! Sing ye hitherto!
The Well! princes searched it out; The nobles of the people have digged it; By their decree, by their act of government, So, after the wilderness, was Mattanah!And after Mattanah were Nahaliel! And after Nahaliel were Bamoth! And after Bamoth was the valley; Where, in the country of Moab, Appeareth the top of Pisgah, Which is over against Jeshimon. See Dr. Kennicott's Remarks upon Select Passages in the Old Testament.
Concise Bible Commentary
Patriarchs and Prophets, 433-8
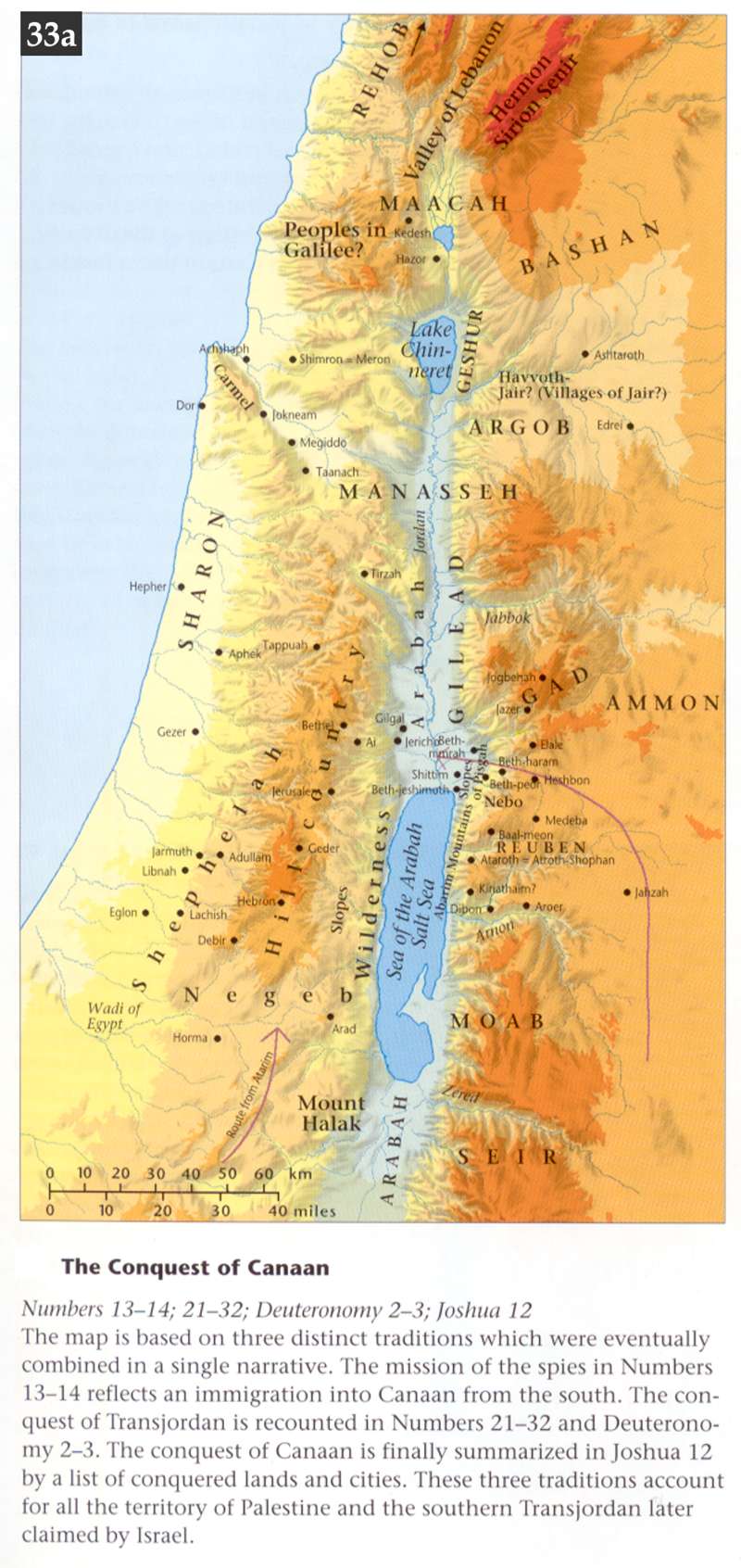
After passing to the south of Edom, the Israelites turned northward, and again set their faces toward the Promised Land. Their route now lay over a vast, elevated plain, swept by cool, fresh breezes from the hills. It was a welcome change from the parched valley through which they had been traveling, and they pressed forward, buoyant and hopeful. Having crossed the brook Zered, they passed to the east of the land of Moab; for the command had been given, “Distress not the Moabites, neither contend with them in battle: for I will not give thee of their land for a possession; because I have given Ar unto the children of Lot.” And the same direction was repeated concerning the Ammonites, who were also descendants of Lot. PP 433.1
Still pushing northward, the hosts of Israel soon reached the country of the Amorites. This strong and warlike people originally occupied the southern part of the land of Canaan; but, increasing in numbers, they crossed the Jordan, made war upon the Moabites, and gained possession of a portion of their territory. Here they had settled, holding undisputed sway over all the land from the Arnon as far north as the Jabbok. The route to the Jordan which the Israelites desired to pursue lay directly through this territory, and Moses sent a friendly message to Sihon, the Amorite king, at his capital: “Let me pass through thy land: I will go along by the highway, I will neither turn unto the right hand nor to the left. Thou shalt sell me meat for money, that I may eat; and give me water for money, that I may drink: only I will pass through on my feet.” The answer was a decided refusal, and all the hosts of the Amorites were summoned to oppose the progress of the invaders. This formidable army struck terror to the Israelites, who were poorly prepared for an encounter with well-armed and well-disciplined forces. So far as skill in warfare was concerned, their enemies had the advantage. To all human appearance, a speedy end would be made of Israel. PP 433.2
Read in context »Patriarchs and Prophets, 453
With joyful hearts and renewed faith in God, the victorious armies of Israel had returned from Bashan. They had already gained possession of a valuable territory, and they were confident of the immediate conquest of Canaan. Only the river Jordan lay between them and the Promised Land. Just across the river was a rich plain, covered with verdure, watered with streams from copious fountains, and shaded by luxuriant palm trees. On the western border of the plain rose the towers and palaces of Jericho, so embosomed in its palm-tree groves that it was called “the city of palm trees.” PP 453.1
On the eastern side of Jordan, between the river and the high tableland which they had been traversing, was also a plain, several miles in width and extending some distance along the river. This sheltered valley had the climate of the tropics; here flourished the shittim, or acacia, tree, giving to the plain the name, “Vale of Shittim.” It was here that the Israelites encamped, and in the acacia groves by the riverside they found an agreeable retreat. PP 453.2
But amid these attractive surroundings they were to encounter an evil more deadly than mighty hosts of armed men or the wild beasts of the wilderness. That country, so rich in natural advantages, had been defiled by the inhabitants. In the public worship of Baal, the leading deity, the most degrading and iniquitous scenes were constantly enacted. On every side were places noted for idolatry and licentiousness, the very names being suggestive of the vileness and corruption of the people. PP 453.3
These surroundings exerted a polluting influence upon the Israelites. Their minds became familiar with the vile thoughts constantly suggested; their life of ease and inaction produced its demoralizing effect; and almost unconsciously to themselves they were departing from God and coming into a condition where they would fall an easy prey to temptation. PP 453.4
Read in context »Patriarchs and Prophets, 485
This exercise of divine power in behalf of Israel was designed also to increase the fear with which they were regarded by the surrounding nations, and thus prepare the way for their easier and complete triumph. When the tidings that God had stayed the waters of Jordan before the children of Israel, reached the kings of the Amorites and of the Canaanites, their hearts melted with fear. The Hebrews had already slain the five kings of Midian, the powerful Sihon, king of the Amorites, and Og of Bashan, and now the passage over the swollen and impetuous Jordan filled all the surrounding nations with terror. To the Canaanites, to all Israel, and to Joshua himself, unmistakable evidence had been given that the living God, the King of heaven and earth, was among His people, and that He would not fail them nor forsake them. PP 485.1
A short distance from Jordan the Hebrews made their first encampment in Canaan. Here Joshua “circumcised the children of Israel;” “and the children of Israel encamped in Gilgal, and kept the Passover.” The suspension of the rite of circumcision since the rebellion at Kadesh had been a constant witness to Israel that their covenant with God, of which it was the appointed symbol, had been broken. And the discontinuance of the Passover, the memorial of their deliverance from Egypt, had been an evidence of the Lord's displeasure at their desire to return to the land of bondage. Now, however, the years of rejection were ended. Once more God acknowledged Israel as His people, and the sign of the covenant was restored. The rite of circumcision was performed upon all the people who had been born in the wilderness. And the Lord declared to Joshua, “This day have I rolled away the reproach of Egypt from off you,” and in allusion to this the place of their encampment was called Gilgal, “a rolling away,” or “rolling off.” PP 485.2
Read in context »