Acts 11:28
Bible Commentary
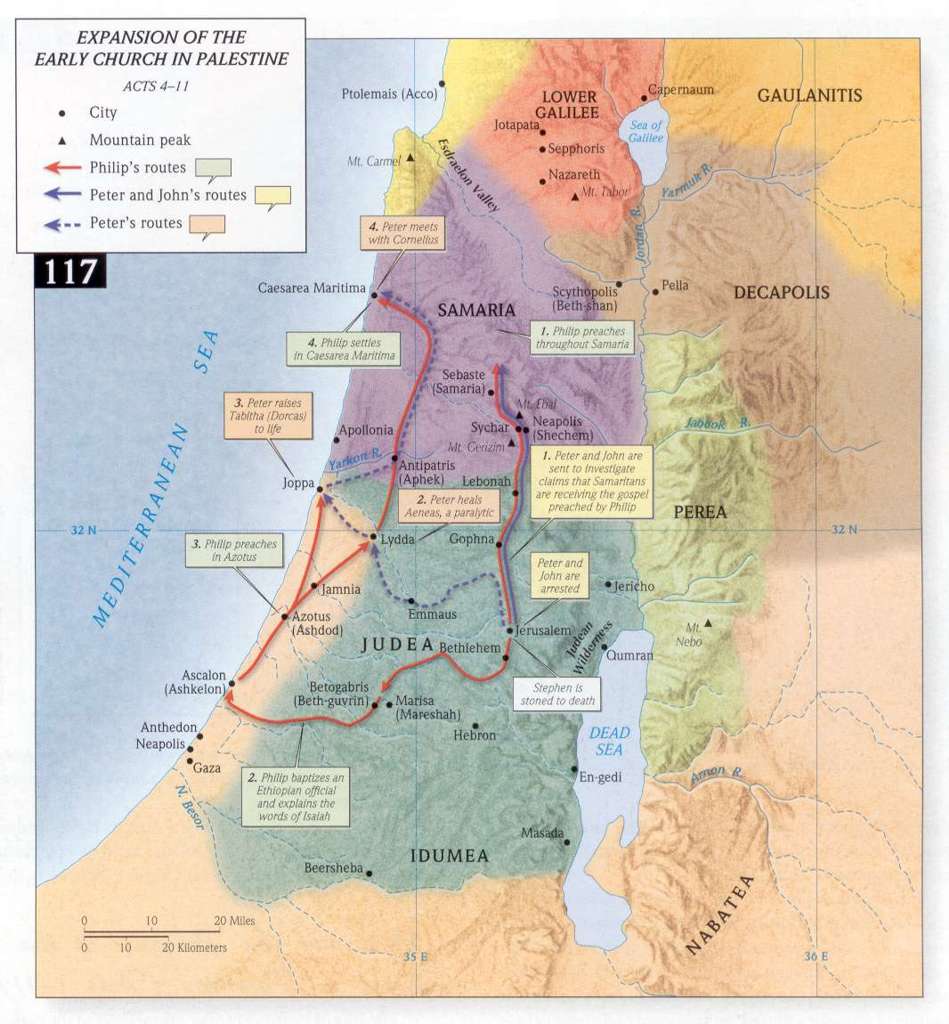
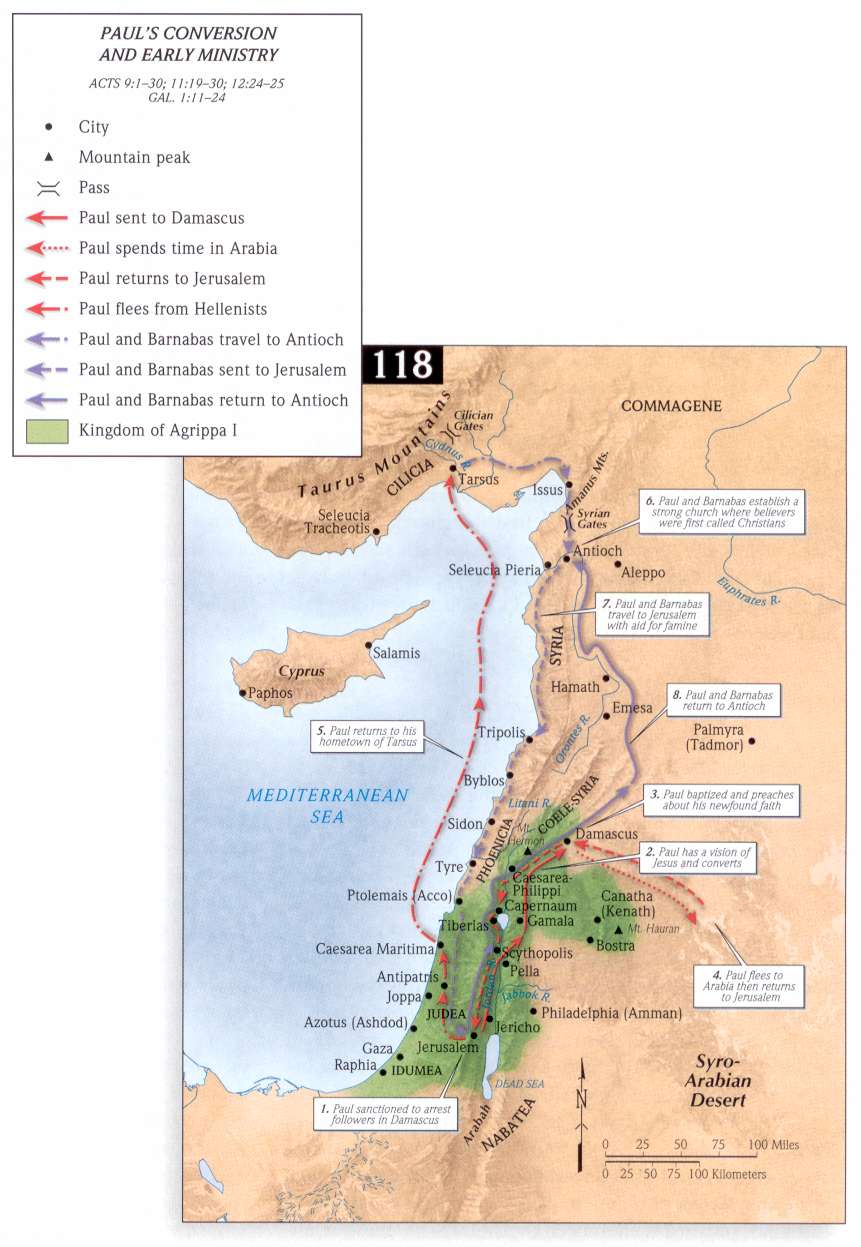
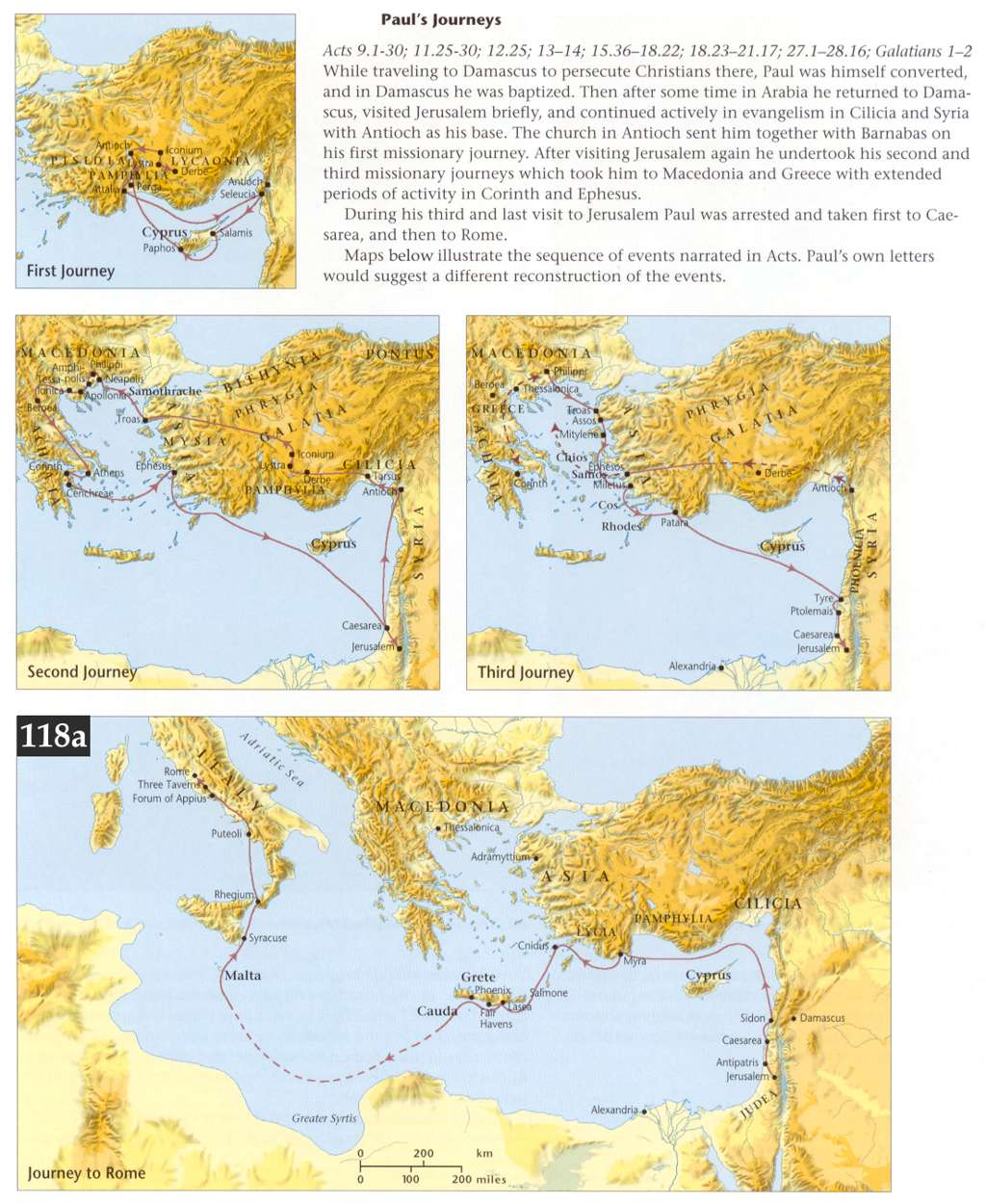
Agabus - This prophet, of whom we know nothing, is once more mentioned, Acts 21:10. He was probably a Jew, but whether converted now to Christianity we cannot tell.
Great dearth throughout all the world - The words εφ 'ὁλην την οικουμενην probably here mean the land of Judea; though sometimes by this phrase the whole Roman empire is intended. In the former sense the disciples appear to have understood it, as the next verse informs us; for they determined to send relief to their brethren in Judea, which they could not have done had the famine been general. It does not appear that they expected it to extend even to Antioch in Syria, where they then were, else they would have thought of making provision for themselves.
It is well known from history that there were several famines in the reign of Claudius. Dion Cassius, lib. lx., mentions a severe famine in the first and second year of the reign of Claudius, which was sorely felt in Rome itself. This famine, it is supposed, induced Claudius to build a port at Ostia, for the more regular supply of Rome with provisions.
A second famine happened about the fourth year of this reign, which continued for several years, and greatly afflicted the land of Judea. Several authors notice this, but particularly Josephus, Ant. lib. xx. cap. 5, sect. 2, where, having mentioned Tiberius Alexander as succeeding to the procuratorship in the place of Cuspius Fadus, he says that, "during the government of these procurators, a great famine afflicted Judea." Επι τουτοις δη και τον μεγαν λιμον κατα την Ιουδαιαν συνεβη γενεσθαι .
A third famine is mentioned by Eusebius, in An. Abrahami, which commences with the calends of October, a.d. 48, which was so powerful "in Greece that a modius (about half a bushel of grain) was sold for six drachms," about three shillings and sixpence English. Vid. Euseb. in Chron. edit. Scalig. The same author mentions another famine in Rome, in the tenth year of Claudius, of which Orosius gives the details, lib. vii.
A fourth famine, which took place in the eleventh year of Claudius, is mentioned by Tacitus, Annal. lib. xii. sect. 43, in which there was so great a dearth of provisions, and famine in consequence, that it was esteemed a Divine judgment. Frugrum quoque egestas, et orta ex ea fames, in prodigium accipiebatur. At this time, the same author tells us, that in all the stores of Rome there were no more than fifteen days' provision; and, had not the winter been uncommonly mild, the utmost distress and misery must have prevailed.
It may now be inquired, to which of these famines in the reign of Claudius does the prophecy of Agabus refer? Most learned men are of opinion that the famine of which Agabus prophesied was that mentioned above, which took place in the fourth year of this emperor. a.d. 47. This famine is particularly mentioned by Josephus, Ant. lib xx. cap. 2, sect. 5, who describes it as "a very great famine, in which many died for want of food." - "That Helena, queen of Adiabene, who had embraced the Jewish religion, sent some of her servants to Alexandria, to buy a great quantity of corn; and others of them to Cyprus, to buy a cargo of dried figs, which she distributed to those who were in want." And in cap. 5, sect. 2, he says that this happened" when Tiberius Alexander succeeded Cuspids Fadus; and that under these procurators the famine happened in which Queen Helena, at a vast expense, procured relief to the Jews." Dr. Hudson's note on this passage in Josephus deserves to be copied: "This," says he, "is that famine foretold by Agabus, Acts 11:28, which happened when Claudius was consul the fourth time, (a.d. 47), and not that which happened when Claudius was consul the second time, and Caecina was his colleague, (a.d. 42), as Scaliger says, upon Eusebius, p. 174. Now when Josephus had said, a little after, cap. 5, sect. 2, that Tiberius Alexander succeeded Cuspius Fadus as procurator, he immediately subjoins, under these procurators there happened a great famine in Judea." From this it is evident that this famine must have continued several years, as it existed under both these procurators. Fadus, says Mr. Whiston, was not sent into Judea till after the death of Agrippa, i.e. towards the end of the fourth year of Claudius, in the end of a.d. 44, or beginning of 45. So that this famine, foretold by Agabus, happened on the fifth, sixth, and seventh years of Claudius, a.d. 45, 46, and 47. See Whiston's Josephus; and see Krebs' Observat. in Nov. Test. on this place.
Notes on the Whole Bible
Named Agabus - This man is mentioned but in one other place in the New Testament. In Acts 21:10-11, he is referred to as having foretold that Paul would be delivered into the hands of the Gentiles. It is not expressly said that he was a Christian, but the connection seems to imply that he was.
And signified - See John 12:33. The word usually denotes “to indicate by signs, or with a degree of obscurity and uncertainty, not to declare in explicit language.” But here it seems to denote simply “to foretell, to predict.”
By the Spirit - Under the influence of the Spirit. He was inspired.
Great dearth - A great famine.
Throughout all the world - The word used here οἰκουμένην oikoumenēnusually denotes “the inhabitable world, the parts of the earth which are cultivated and occupied.” It is sometimes used, however, to denote “an entire land or country,” in contradistinction from the parts of it: thus, to denote “the whole of the land of Palestine” in distinction from its parts; or to denote that an event would have reference to all the land, and not be confined to one or more parts, as Galilee, Samaria, etc. See the notes on Luke 2:1. The meaning of this prophecy evidently is, that the famine would be extensive; that it would not be confined to a single province or region, but that it would extend so far as that it might be called “general.” In fact, though the famine was particularly severe in Judea, it extended much further. This prediction was uttered not long after the conversion of Saul, and probably, therefore, about the year, 38 a.d. or 40 a.d. Dr. Lardner has attempted to show that the prophecy had reference only to the land of Judea, though in fact there were famines in other places (Lardher‘s Works, vol. 1, pp. 253,254, edit. London, 1829). Which came to pass … - This is one of the few instances in which the sacred writers in the New Testament affirm the fulfillment of a prophecy. The history having been written after the event, it was natural to give a passing notice of the fulfillment. In the days of Claudius Caesar - The Roman emperor. He began his reign in 41 a.d., and he reigned for 13 years. He was at last poisoned by one of his wives, Agrippina, who wished to raise her son Nero to the throne. During his reign no less than four different famines are mentioned by ancient writers, one of which was particularly severe in Judea, and was the one, doubtless, to which the sacred writer here refers: (1) The first happened at Rome, and occurred in the first or second year of the reign of Claudius. It arose from the difficulties of importing provisions from abroad. It is mentioned by Dio, whose words are these: “There being a great famine, he (Claudius) not only took care for a present supply, but provided also for the time to come.” He then proceeds to state the great expense which Claudius was at in making a good port at the mouth of the Tiber, and a convenient passage from thence up to the city (did, lib. Ix. p. 671,672; see also Suetonius, Claudius, cap. 20). (2) asecond famine is mentioned as having been particularly severe in Greece. Of this famine Eusebius speaks in his Chronicon, p. 204: “There was a great famine in Greece, in which a modius of wheat (about half a bushel) was sold for six drachmas.” This famine is said by Eusebius to have occurred in the ninth year of the reign of Claudius. (3) in the latter part of his reign, 51 a.d., there was another famine at Rome, mentioned by Suetonius (Claudius, cap. 18), and by Tacitus (Ann., John 12:43). Of this, Tacitus says that it was so severe that it was deemed to be a divine judgment. (4) afourth famine is mentioned as having occurred particularly in Judea. This is described by Josephus (Antiq., book 20, chapter 2, section 5). “A famine,” says he, “did oppress them at the time (in the time of Claudius); and many people died for the lack of what was necessary to procure food withal. Queen Helena sent some of her servants to Alexandria with money to buy a great quantity of grain, and others of them to Cyprus to bring a cargo of dried figs.” This famine is described as having continued under the two procurators of Judea, Tiberius Alexander and Cassius Fadus. Fadus was sent into Judea, on the death of Agrippa, about the fourth year of the reign of Claudius, and the famine, therefore, continued probably during the fifth, sixth, and seventh years of the reign of Claudius. See the note in Whiston‘s Josephus, Antiq., book 20, chapter 2, section 5; also Lardner as quoted above. Of this famine, or of the want consequent on the famine, repeated mention is made in the New Testament.
Concise Bible Commentary
Testimonies for the Church, vol. 6, 271
Through circumstances some who love and obey God become poor. Some are not careful; they do not know how to manage. Others are poor through sickness and misfortune. Whatever the cause, they are in need, and to help them is an important line of missionary work. 6T 271.1
All our churches should have a care for their own poor. Our love for God is to be expressed in doing good to the needy and suffering of the household of faith whose necessities come to our knowledge and require our care. Every soul is under special obligation to God to notice His worthy poor with particular compassion. Under no consideration are these to be passed by. 6T 271.2
Paul wrote to the Corinthian church: “Moreover, brethren, we do you to wit of the grace of God bestowed on the churches of Macedonia; how that in a great trial of affliction the abundance of their joy and their deep poverty abounded unto the riches of their liberality. For to their power, I bear record, yea, and beyond their power they were willing of themselves; praying us with much entreaty that we would receive the gift, and take upon us the fellowship of the ministering to the saints. And this they did, not as we hoped, but first gave their own selves to the Lord, and unto us by the will of God. Insomuch that we desired Titus, that as he had begun, so he would also finish in you the same grace also.” 6T 271.3
Read in context »